Mocht u de informatie op onze website kanker-actueel.nl waarderen dan wilt u ons misschien ondersteunen met een donatie?
Ons rekeningnummer is: RABO 37.29.31.138 t.n.v. Stichting Gezondheid Actueel in Terneuzen. Onze IBANcode is NL79 RABO 0372 9311 38
Als donateur kunt u ook korting krijgen bij verschillende bedrijven. En we hebben een ANBI status
10 mei 2020: Aanvullend op onderstaande studie blijkt dat Afatinib ook effectief kan zijn bij niet-kleincellige longkanker met andere mutaties en samengestelde mutaties dan de bekende EGFR-mutaties waarvoor Afatinib uitstekend werkzaam is. Afatinib heeft ook een brede activiteit tegen andere ongebruikelijke EGFR-mutaties en sommige exon 20-inserties. Bewijst deze studie: Afatinib for the Treatment of NSCLC Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations: A Database of 693 Cases die gratis is in te zien.
De verschillende voorkomende mutaties en beschikbare baselinekenmerken worden getoond in Table 2.
Over het geheel genomen had:
- 29% van de patiënten die in de analyse waren opgenomen een tumor met een belangrijke soms voorkomende mutatie (G719X, L861Q, S768I),
- 25% had een T790M-mutatie (voornamelijk in de EGFR TKI –Voorbehandelde patiënten),
- 21% had een insertie van exon 20,
- 13% had andere soms voorkomende EGFR-mutaties
- 12% had een samengestelde mutatie.
De resultaten van afatinib bij de verschillende mutaties staat vermeld in (Table 3).
Abstract staat onderaan artikel.
Zie ook dit artikel:
13 februari 2019: Aanvullend op onderstaande informatie (scroll verder naar onderen) een nieuwe recente studiepublicatie over effect van afatinib bij longkanker met HER2 mutaties pos.:
Met deze resultaten, waarbij opvalt dat maar weinig longkankerpatiënten een Her2 positieve mutatie hebben (1 procent ) maar als ze die hebben kan afatinib dus blijkbaar wel goed werken. Want van de 23 patienten bereikten er alsnog drie (13 procent) een gedeeltelijke respons van dus minimaal 50 procent vermindering van tumoromvang en aantal en meer dan de helft 13 patienten (57 procent) bereikten minimaal stabiele ziekte. En de mediane overall overleving steeg naar 23 maanden wat voor deze groep van patienten echt lang is.
Hier het abstract van de studie. Zie ook verderop in dit artikel meer over effect van afatinib bij longkanker in het algemeen dus zonder gekoppeld te zijn aan een bepaalde mutatie.
Introduction
HER2 mutations occur in 1–3% of lung adenocarcinomas. With increasing use of next-generation sequencing at diagnosis, more patients with HER2-mutant tumours present for treatment. Few data are available to describe the clinical course and outcomes of these patients when treated with afatinib, a pan-HER inhibitor.
Methods
We identified patients with metastatic or recurrent HER2-mutant lung adenocarcinomas treated with afatinib among seven institutions across Europe, Australia, and North America between 2009 and 2017. We determined the partial response rate to afatinib, types of HER2 mutations, duration of response, time on treatment, and survival.
Results
We collected information on 27 patients with stage IV or recurrent HER2-mutant lung adenocarcinomas treated with afatinib. Of 23 patients evaluable for response, three partial responses were noted (13%, 95% confidence interval 4–33%). In addition, 57% of patients (13/23) had stable disease, and 30% (7/23) had progressive disease. We documented partial responses in patients with HER2 exon 20 insertions, including two with YVMA insertion and one with VAG insertion. Two patients with partial responses were previously treated with trastuzumab and pertuzumab. Median duration of response to afatinib was 6 months (range 5–10); median time on treatment was 3 months (range 1–30) and median overall survival from the date of diagnosis of metastatic or recurrent disease was 23 months (95% CI 18–53 months).
Conclusions
Afatinib is modestly active in patients with HER2-mutant lung adenocarcinomas, including responses after progression on prior HER2-targeted therapies. However, investigations into the biology of HER2-mutant lung adenocarcinomas and development of better HER2-directed therapies are warranted.
2 februari 2016: Bron: Journal of Thoracic Oncology
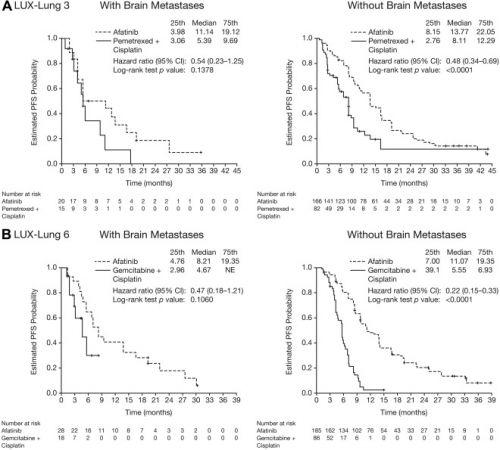
Uit twee onafhankelijk van elkaar lopende studies met afatinib als monobehandeling als eerstelijnsbehandeling bij vergevorderde longkanker met specifiek uitzaaiingen in de hersenen en bij vergevorderde slokdarmkanker met uitzaaiingen in de hersenen, allen met EGFR positieve expressie blijkt dat afatinib alsnog voor opmerkelijke resultaten zorgt. In vergelijking met de chemo combinaties Alimta en cisplatin of cisplatin en gemzar - gemcitabine blijkt afitinib alleen voor langere progressievrije ziekte te zorgen bij patiënten met hersentumoren (8.2 versus 5.4 maanden; hazard ratio = 0.50, P = .0297), en de overall respons, dus dat de behandeling aansloeg, was veruit superieur voor afitinib in vergelijking met de chemo of placebo (73% versus 25%). Al eerder heeft afatinib bewezen bij longkanker voor goede resultaten te kunnen zorgen, ook die zonder uitzaaiingen in de hersenen. Zie deze grafiek:
Deze niuewe analyse is een tussenevaluatie van lopende studies waaruit patiënten met hersenuitzaaiingen zijn geselecteerd. Namelijk deze: BIBW 2992 (Afatinib) vs Gemcitabine-cisplatin in 1st Line Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) en deze bij vergevorderde slokdarmkanker: A Phase II Trial of Afatinib in Patients With Metastatic or Recurrent Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Esophagus
Sleutelpunten uit de studie die een analyse maakte van de twee studies voor specifiek die patiënten met hersenuitzaaiingen vanuit longkanker:
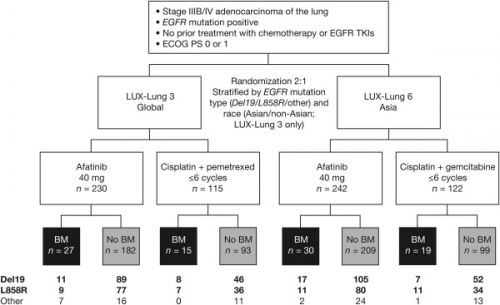
- 35 uit 345 (10.1%) gerandomiseerd ingedeelde patiënten in de LUX-Lung 3 studie en 46 uit 364 (12.6%) in de LUX-Lung 6 studie hadden hersenuitzaaiingen bij aanvang van de studie en de algemeen voorkomende (Del19 en L858R) EGFR mutaties.
- De resultaten uit beide studies samengevoegd gaf afatinib, vergeleken met chemotherapie een statistisch significant betere progressievrije tijd. En de respons, aanslaan van de behandeling, was heel veel beter voor afatinib in vergelijking met chemotherapie.
- het bijwerkingen profiel voor afatinib bij patiënten met hersenuitzaaiingen lag gelijk aan die bij patiënten zonder hersenuitzaaiingen en waren zonder ernstige veiligheidsrisico's.
Het volledige studieverslag van First-Line Afatinib versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer and Common Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutations and Brain Metastases is gratis in te zien met interessante grafieken.
Hier het abstract van de studie:
Findings from two studies lend support to the clinical activity of afatinib in EGFR mutation–positive patients with NSCLC and asymptomatic brain metastases.
First-Line Afatinib versus Chemotherapy in Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer and Common Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutations and Brain Metastases
Presented in part at the 15th World Conference on Lung Cancer in Sydney, Australia, October 27–30, 2013.
Abstract
Introduction
Metastatic spread to the brain is common in patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but these patients are generally excluded from prospective clinical trials. The studies, phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 3) and a randomized, open-label, phase III study of BIBW 2992 versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with stage IIIB or IV adenocarcinoma of the lung harbouring an EGFR activating mutation (LUX-Lung 6) investigated first-line afatinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR) mutation-positive patients with NSCLC and included patients with brain metastases; prespecified subgroup analyses are assessed in this article.
Methods
For both LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6, prespecified subgroup analyses of progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival, and objective response rate were undertaken in patients with asymptomatic brain metastases at baseline (n = 35 and n = 46, respectively). Post hoc analyses of clinical outcomes was undertaken in the combined data set (n = 81).
Results
In both studies, there was a trend toward improved PFS with afatinib versus chemotherapy in patients with brain metastases (LUX-Lung 3: 11.1 versus 5.4 months, hazard ratio = 0.54, p = 0.1378; LUX-Lung 6: 8.2 versus 4.7 months, HR = 0.47, p = 0.1060). The magnitude of PFS improvement with afatinib was similar to that observed in patients without brain metastases. In combined analysis, PFS was significantly improved with afatinib versus with chemotherapy in patients with brain metastases (8.2 versus 5.4 months; HR, 0.50; p = 0.0297). Afatinib significantly improved the objective response rate versus chemotherapy in patients with brain metastases. Safety findings were consistent with previous reports.
Conclusions
These findings lend support to the clinical activity of afatinib in EGFR mutation–positive patients with NSCLC and asymptomatic brain metastases.
References
- Langer, C.J., Mehta, M.P. Current management of brain metastases, with a focus on systemic options. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6207–6219.
- Eichler, A.F., Loeffler, J.S. Multidisciplinary management of brain metastases. Oncologist. 2007;12:884–898.
- Fan, Y., Huang, Z., Fang, L. et al, Chemotherapy and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for treatment of brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: survival analysis in 210 patients. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1789–1803.
- Hoffknecht, P., Tufman, A., Wehler, T. et al, Efficacy of the irreversible ErbB family blocker afatinib in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-pretreated non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases or leptomeningeal disease. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10:156–163.
- Abstract
- | Full Text
- | Full Text PDF
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (11)
- Khuntia, D., Brown, P., Li, J. et al, Whole-brain radiotherapy in the management of brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1295–1304.
- Ruderman, N., Hall, R. Use of glucocorticoids in the palliative treatment of metastatic brain tumors. Cancer. 1965;18:298–306.
- Zimm, S., Wampler, G.L., Stablein, D. et al, Intracerebral metastases in solid-tumor patients: natural history and results of treatment. Cancer. 1981;48:384–394.
- Hendriks, L.E., Smit, E.F., Vosse, B.A. et al, EGFR mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients: more prone to development of bone and brain metastases?. Lung Cancer. 2014;84:86–91.
- Abstract
- | Full Text
- | Full Text PDF
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (9)
- Bhatt, V.R., Kedia, S., Kessinger, A. et al, Brain metastasis in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3162–3164.
- Ali, A., Goffin, J.R., Arnold, A. et al, Survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer after a diagnosis of brain metastases. Curr Oncol. 2013;20:e300–e306.
- CrossRef
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (6)
- Iuchi, T., Shingyoji, M., Sakaida, T. et al, Phase II trial of gefitinib alone without radiation therapy for Japanese patients with brain metastases from EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2013;82:282–287.
- Abstract
- | Full Text
- | Full Text PDF
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (21)
- Park, S.J., Kim, H.T., Lee, D.H. et al, Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring either exon 19 or 21 mutation. Lung Cancer. 2012;77:556–560.
- Abstract
- | Full Text
- | Full Text PDF
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (62)
- Porta, R., Sanchez-Torres, J.M., Paz-Ares, L. et al, Brain metastases from lung cancer responding to erlotinib: the importance of EGFR mutation. Eur Respir J. 2011;37:624–631.
- Song, Z., Zhang, Y. Gefitinib and erlotinib for non-small cell lung cancer patients who fail to respond to radiotherapy for brain metastases. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21:591–595.
- Wu, Y.L., Zhou, C., Cheng, Y. et al, Erlotinib as second-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and asymptomatic brain metastases: a phase II study (CTONG-0803). Ann Oncol. 2013;24:993–999.
- Li, D., Ambrogio, L., Shimamura, T. et al, BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene. 2008;27:4702–4711.
- Solca, F., Dahl, G., Zoephel, A. et al, Target binding properties and cellular activity of afatinib (BIBW 2992), an irreversible ErbB family blocker. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012;343:342–350.
- Sequist, L.V., Yang, J.C., Yamamoto, N. et al, Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3327–3334.
- Wu, Y.L., Zhou, C., Hu, C.P. et al, Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:213–222.
- Abstract
- | Full Text
- | Full Text PDF
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (231)
- Yang, J.C., Hirsh, V., Schuler, M. et al, Symptom control and quality of life in LUX-Lung 3: a phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin/pemetrexed in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3342–3350.
- Yang, J.C., Wu, Y.L., Schuler, M. et al, Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:141–151.
- Abstract
- | Full Text
- | Full Text PDF
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (81)
- Yang, J.C., Shih, J.Y., Su, W.C. et al, Afatinib for patients with lung adenocarcinoma and epidermal growth factor receptor mutations (LUX-Lung 2): a phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:539–548.
- Abstract
- | Full Text
- | Full Text PDF
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (183)
- Campas, C., Castaner, R., Bolos, J. BIBW-2992. Dual EGFR/HER2 inhibitor oncolytic. Drugs Fut. 2008;33:649.
- Yang, J.C., Sequist, L.V., Geater, S.L. et al, Activity of afatinib in uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations: findings from three trials of afatinib in EGFR mutation-positive lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8:S139.
- European Medicines Agency. Giotrif—Summary of Product Characteristics, Annex 1. 2013. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/002280/WC500152392.pdf. Accessed June 18, 2015.
- Food and Drug Administration. Afatinib. 2015. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm360574.htm. Accessed June 18, 2015.
- Eisenhauer, E.A., Therasse, P., Bogaerts, J. et al, New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228–247.
- van, V.M., Kal, H.B., Taphoorn, M.J. et al, Changes in blood-brain barrier permeability induced by radiotherapy: implications for timing of chemotherapy? (Review). Oncol Rep. 2002;9:683–688.
- Dhruva, N., Socinski, M.A. Carcinomatous meningitis in non-small-cell lung cancer: response to high-dose erlotinib. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:e31–e32.
- Grommes, C., Oxnard, G.R., Kris, M.G. et al, “Pulsatile” high-dose weekly erlotinib for CNS metastases from EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13:1364–1369.
- Hata, A., Kaji, R., Fujita, S. et al, High-dose erlotinib for refractory brain metastases in a patient with relapsed non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:653–654.
- Abstract
- | Full Text
- | Full Text PDF
- | PubMed
- | Scopus (30)
- Jackman, D.M., Holmes, A.J., Lindeman, N. et al, Response and resistance in a non–small-cell lung cancer patient with an epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and leptomeningeal metastases treated with high-dose gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4517–4520.
- Jackman, D.M., Mach, S.L., Heng, J.C. et al, Pulsed dosing of erlotinib for central nervous system (CNS) progression in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). ()J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:8116.
Drs. Schuler and Wu contributed equally to this work.
Disclosure: Dr. Schuler has received personal fees from Novartis, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Lilly and grants from Novartis and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Wu has received speaker fees from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Roche, and Sanofi. Dr. Hirsh reports advisory board participation for Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. O’Byrne has received honoraria for advisory board and speakers’ bureau work; travel, accommodation, and registration expenses for meetings from Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp Dohme, Lilly Oncology, AstraZeneca, Roche, Pfizer and BMS; and writing assistance from Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, and BMS. Dr. Mok has received personal fees from AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, Lilly, Merck Serono, Eisai, BMS, AVEO, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, Clovis Oncology, Amgen, Janssen, BioMarin Pharmaceuticals, SFJ Pharmaceuticals, ACEA Biosciences, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Popat has been a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Sequist reports that her institution received a grant from Boehringer Ingelheim to support the study; has performed noncompensated consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim, Clovis Oncology, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Merrimack, Taiho, and Genentech; and has received personal fees from Ariad for consulting. Drs. Massey and Zazulina are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Yang has received personal fees for presentations and advisory board participation from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Roche, Genentech, Chugai, Eli Lilly, and MSD and personal fees for advisory board participation only from Merck Serono, Clovis Oncology, Pfizer, Novartis, Ono pharmaceutical, Astellas, Innopharma, Celgene and Bayer. The remaining author declare no conflict of interest.
Trial registration information located at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ identifiers: NCT01121393, NCT00949650.
afatinib demonstrated durable responses in some patients with exon 20 insertions. Generally, afatinib demonstrated broad activity across very rare (other) mutations, consistent with preclinical findings
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Afatinib verlengt progressie vrije overleving bij patiënten met gevorderde longkanker met positieve EGFR mutaties in vergelijking met cisplatin en pemetrexed - Alimta en ook vergeleken met placebo
- Giotrif®(afatinib) gevolgd door osimertinib laat mediane algehele overleving zien van bijna vier jaar bij patiënten met EGFR T790M-positieve niet-kleincellige longkanker (NSCLC) en DEL19 mutatie
- Tyrosine Kinase remmers (TKI) bij longkanker met EGFR mutaties. Een overzicht van artikelen van verschillende TKI remmers.





Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Afatinib, een Tyrosine kinase remmer geeft goede resultaten bij longkankerpatiënten met uitzaaiingen in de hersenen in vergelijking met chemo en placebo"