Aan dit artikel is vele uren gewerkt. Opzoeken, vertalen, op de website plaatsen enz. Als u ons wilt ondersteunen dan kan dat via een al of niet anonieme donatie. Elk bedrag is welkom hoe klein ook. Klik hier als u ons wilt helpen kanker-actueel online te houden Wij zijn een ANBI organisatie en dus is uw donatie in principe aftrekbaar voor de belasting.
2 mei 2019:
zie ook dit artikel:
10 januari 2016: lees ook dit artikel:
17 mei 2015: 2015 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium en N Engl J Med. 2014 Sep 11;371(11):1028-38. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1315815. Epub 2014 Sep 3.
AR-V7 (AR) een zogeheten androgene receptor marker (RNA marker) van in bloed circulerende tumorcellen heeft grote voorspellende waarde welke behandeling / medicijnen ingezet kunnen worden bij hormoonresistente gevorderde prostaatkanker. De circulerende AR-V7 positieve tumorcellen voorspelt of iemand gevoelig is voor chemo met docetaxel of cabazitaxel (Jevtana) of beter gezegd resistent is voor enzalutamide (Xtandi) en abiraterone (Zytiga).
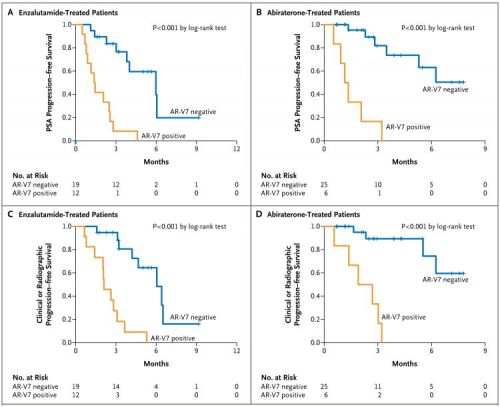
Wie in bloed circulerende tumorcellen heeft met AR-V7 positief lijkt ongevoelig voor abiraterone en enzalutamide en zou nog iets kunnen profiteren van chemo al is dat verschil niet erg groot met nog geen twee maanden mediane overleving erbij, 5,1 versus 6,9 maanden. Opmerkelijk ook dat de onderzoekers opmerken dat met name mannen die zwaar en intensieve hormoontherapie hebben gehad een AR-V7 afwijking laten zien en ongevoelig worden voor abiraterone en enzalutamide.
Een alternatief voor hormoontherapie in een eerder stadium van prostaatkanker kan prostasol zijn.
Dit blijkt uit verschillende studies gepresenteerd op het Genitourinary Cancers Symposium 2015 door hoofdauteur Emmanuel Antonarakis, MD, of Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.
In een recente studie werden 37 mannen met uitgezaaide hormoonresistente prostaatkanker behandeld met een taxane chemo en geanalyseerd op de marker; 17 van de 37 mannen waren AR-V7 positief. Alle mannen reageerden gelijk op de chemotherapie, ongeacht hun AR-V7 status. Reactie op hun PSA - Prostate-specific antigen met 50% of meer PSA daling vanaf de start verschilde wel, namelijk 41% bij de AR-V7–positieve groep en 65% bij de AR-V7–negatieve groep.
Mediane PSA–progressie-vrije tijd was vergelijkbaar tussen de twee groepen hoewel deze langer duurde bij de AR-V7 positieve groep: 4.5 maanden versus 6.2 maanden, respectievelijk. Mediane progressie-vrije overleving was in AR-V7–positieve en AR-V7–negatieve patienten, behandeld met een taxane chemo: 5.1 maanden and 6.9 maanden, respectievelijk. Deze verschillen waren niet statistisch significant maar wel dus in het voordeel van AR-V7 positief.
“Wanneer we deze gegevens invoerden en vergeleken met de 62 mannen uit de eerdere abiraterone/enzalutamide studie, werd duidelijk dat de klinische resultaten bij de AR-V7 positieve groep superieur waren emt een taxane chemo in vergelijking met abiraterone/enzalutamide. De resultaten bij AR-V7 negatief verschilde niet tussen de behandelingen,” aldus Dr. Antonarakis.
Bv. in de AR-V7–positieve mannen, een reactie met PSA daling werd gezien bij 41% in de taxane behandelgroep en 0% in de abiraterone/enzalutamide groep. Mediane PSA–progressie-vrije tijd en mediane progressie-vrije overleving waren significant langer bij met taxane behandelde mannen vergeleken met de mannen uit de abiraterone/enzalutamide groep (P = .001 and P = .003, respectively).
Dr. Antonarakis merkt ook op dat ca. 30% van de mannen met hormoonresistente prostaatkanker een AR-V7 afwijking ontwikkelen. Er wordt veronderstelt dat dit vaker vorokomt bij mannen die langduriger en intensievere hormoontherapie hebben gekregen, al;dus dr. Antonarakis.
Eerder is vorig jaar al een studie gepubliceerd in NEJM over ditzelfde onderwerp, zie ook dit artikel: https://kanker-actueel.nl/NL/bloedmarker-ar-v7-lijkt-een-nieuwe-biomarker-die-voorspelt-of-abiraterone-zytiga-of-enzalutamine-xtandi-wel-of-niet-een-werkzaam-medicijn-kan-zijn-voor-uitgezaaide-hormoonresistente-prostaatkanker.html.
Interessant is ook dat er veel commentaar is gegeven op deze bevindingen in verschillende studies. Ik heb al die commentaren niet bekeken maar als u klikt op een van de volgende links kunt u dit zelf lezen:
Comment in
- Resistance to androgen-pathway drugs in prostate cancer. [N Engl J Med. 2014]
- Resistance to androgen-pathway drugs in prostate cancer. [N Engl J Med. 2014]
- Targeting the androgen receptor in prostate cancer--a resilient foe. [N Engl J Med. 2014]
- Re: AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer. [Eur Urol. 2015]
- Prostate cancer: predicting resistance-AR-V7 is a potential biomarker. [Nat Rev Urol. 2014]
- Enzalutamide for treatment of CRPC: rationale for sequencing and potential clinical biomarker for resistance. [Cancer Biol Ther. 2015]
- Resistance to androgen-pathway drugs in prostate cancer. [N Engl J Med. 2014]
- Resistance to androgen-pathway drugs in prostate cancer. [N Engl J Med. 2014]
- Re: AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer. [J Urol. 2015]
Bovenstaande is ontleend aan drie studies waarvan de abstracten hieronder zijn vermeld. Het volledige studierapport: AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer is gratis te lezen of te downloaden.
References
1. Antonarakis ES, et al: 2015 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium. Abstract 138. Presented February 26, 2015.
2. Antonarakis ES, et al: 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting. Abstract 5001. Presented June 1, 2014.
3. Antonarakis ES, et al: N Engl J Med 371:1028-1038, 2014.
Detection of AR-V7 in CTCs from men with mCRPC is not associated with primary resistance to taxane chemotherapy, and such patients may retain sensitivity to taxanes. Further, in AR-V7[+] men, taxanes appear to be more efficacious than abi/enza. AR-V7 may represent a treatment-selection marker in mCRPC.
AR splice variant 7 (AR-V7) and response to taxanes in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
Abstract:
Background: AR-V7 is a truncated form of AR that lacks the ligand-binding domain but remains constitutively active. We previously showed that detection of AR-V7 from circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in men with mCRPC was associated with primary resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone. Here, we hypothesized that AR-V7[+] patients would retain sensitivity to taxane chemotherapy.
Methods: We used a qRT-PCR assay to interrogate CTCs for AR-V7 mRNA in prospectively enrolled patients with mCRPC starting docetaxel or cabazitaxel. We sought associations between AR-V7 status and PSA response rates (the primary endpoint), PSA progression-free survival (PSA-PFS), and clinical/radiographic progression-free survival (PFS). Multivariable regressions were performed to determine the independent effect of AR-V7 status on clinical outcomes. 36 taxane-treated men were required to produce a 2-sided 95% CI for the difference in PSA response rates (between AR-V7[+] and AR-V7[–] men) with an upper bound of 60%, assuming that 30% of men would be AR-V7[+].
Results: 37 taxane-treated patients were enrolled, and 17 (45.9%) had detectable AR-V7 in CTCs. PSA responses were achieved in both AR-V7[+] and AR-V7[–] men (41% vs 65%, P=0.19). Median PSA-PFS was comparable in AR-V7[+] and AR-V7[–] men (4.5 vs 6.2 mo, HR 1.72, P=0.32). Likewise, median PFS was comparable in AR-V7[+] and AR-V7[–] men (5.1 vs 6.9 mo, HR 2.65, P=0.11). After incorporating data from our prior study in 62 abi/enza-treated patients, it was observed that clinical outcomes in AR-V7[+] men were superior with taxanes than with abi/enza, while outcomes did not differ by treatment type in AR-V7[–] men. For example, in AR-V7[+] men, PSA responses were higher in taxane-treated versus abi/enza-treated men (41% vs 0%, P<0.001), and median PSA-PFS and PFS were longer in taxane-treated men (HR for PSA-PFS = 0.19, P=0.001; HR for PFS = 0.21, P=0.003).
Conclusions: Detection of AR-V7 in CTCs from men with mCRPC is not associated with primary resistance to taxane chemotherapy, and such patients may retain sensitivity to taxanes. Further, in AR-V7[+] men, taxanes appear to be more efficacious than abi/enza. AR-V7 may represent a treatment-selection marker in mCRPC.
Detection of AR-V7 in CTCs from men with mCRPC is associated with resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone. AR-V7 status may be used as a biomarker to predict resistance to AR-targeting agents, facilitate treatment selection, and fuel the development AR N-terminal domain inhibitors.
2014 ASCO Annual Meeting
Background: Androgen receptor splice variant-7 (AR-V7) is a truncated form of the androgen receptor that lacks the ligand-binding domain, the target of enzalutamide and abiraterone, but remains constitutively active as a transcription factor. We hypothesized that detection of AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from men with mCRPC may be associated with primary resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone.
Methods: We used quantitative reverse-transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) to interrogate CTCs for the presence or absence of AR-V7 from prospectively enrolled patients with mCRPC initiating treatment with enzalutamide or abiraterone. We examined associations between AR-V7 status and PSA response rates, PSA progression-free survival (PSA-PFS), and clinical/radiographic progression-free survival (PFS). Multivariable Cox regression analyses were performed to determine the independent effect of AR-V7 status on these clinical outcomes. 30 men (per cohort) were required to detect a difference in PSA response rates from 10% (in AR-V7–positive men) to 60% (in AR-V7–negative men), using a 2-sided α=0.10 and β=0.15.
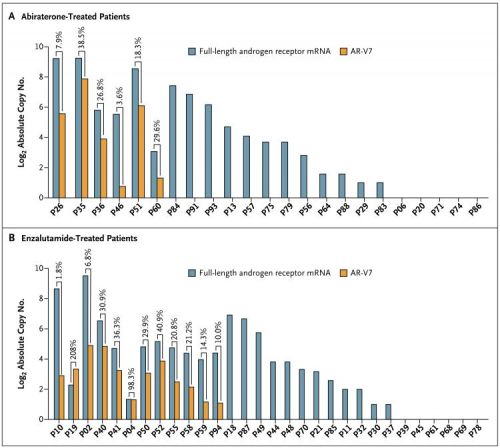
Results: 31 enzalutamide-treated patients and 31 abiraterone-treated patients were enrolled, of which 38.7% and 19.4% had detectable AR-V7 from CTCs, respectively. Among men receiving enzalutamide, AR-V7–positive patients had inferior PSA response rates (0% vs 52.6%, P=0.004), PSA-PFS (median 1.4 vs 5.9 months, P<0.001), and PFS (median 2.1 vs 6.1 months, P<0.001) compared to AR-V7–negative patients. Similarly, among men receiving abiraterone, AR-V7–positive patients had inferior PSA response rates (0% vs 68.0%, P=0.004), PSA-PFS (median 1.3 months vs not reached, P<0.001), and PFS (median 2.3 months vs not reached, P<0.001). The negative prognostic impact of AR-V7 was maintained after adjusting for full-length AR expression levels.
Conclusions: Detection of AR-V7 in CTCs from men with mCRPC is associated with resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone. AR-V7 status may be used as a biomarker to predict resistance to AR-targeting agents, facilitate treatment selection, and fuel the development AR N-terminal domain inhibitors.
Gerelateerde artikelen
- TP53 afwijkingen zijn veel sterkere prognosefactor voor abiraterone en enzalutamide dan Androgyne receptoren expressie (AR-Vf) voor gevorderde uitgezaaide prostaatkanker
- Biomarker AR-V7 voorspelt of abiraterone - Zytiga of enzalutamine - Xtandi wel of niet een werkzaam medicijn kan zijn voor uitgezaaide hormoonresistente prostaatkanker.
- Reguliere oncologie: overzicht van recente ontwikkelingen en belangrijke studies binnen de reguliere oncologie voor prostaatkanker



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "AR-V7 receptor voorspelt welke behandeling zinvol is voor hormoonresistente gevorderde prostaatkanker: chemo of abiraterone en enzalutamide copy 1"