26 januari 2019: lees ook dit artikel:
1 april 2017: Bron: The Lancet
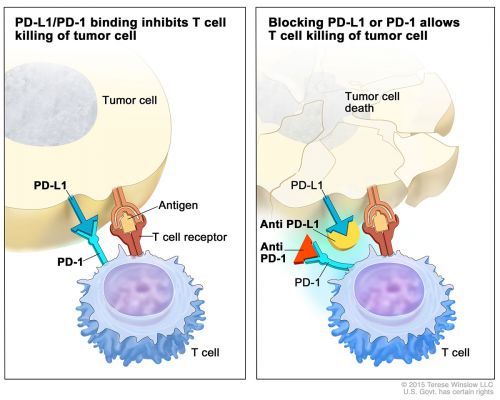
Ook bij mesothelioma - asbestkanker lijkt immuuntherapie met een anti-PD medicijn, in dit geval pembrolizumab uitstekend te werken. In een kleinschalige studie met 25 patiënten die minimaal twee chemokuren en Alimta hadden gehad maar desondanks progressie van hun ziekte vertoonden bleek pembrolizumab alsnog bij 5 patienten (20 procent) voor een PR- gedeeltelijke remissie te zorgen en bij 51 procent voor stabiele ziekte = stilstand van de ziekte. Een uitstekend resultaat natuurlijk, ook omdat mesothelioma als ongeneeslijk bekend staat en de patiënten die aan de studie meededen al meerdere chemo's te verduren hadden gekregen.
Tekst gaat onder beeld verder
Kernpunten uit de studie:
In an interim analysis of the phase IB KEYNOTE-028 trial reported in The Lancet Oncology, Alley et al found that pembrolizumab (Keytruda) treatment produced durable responses in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Clinical safety and activity of pembrolizumab in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (KEYNOTE-028): preliminary results from a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b trial
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30169-9
Summary
Background
Malignant pleural mesothelioma is a highly aggressive cancer with poor prognosis and few treatment options following progression on platinum-containing chemotherapy. We assessed the safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab (an anti-programmed cell death receptor 1 [PD-1] antibody) in advanced solid tumours expressing programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and report here on the interim analysis of the malignant pleural mesothelioma cohort.
Methods
Previously treated patients with PD-L1-positive malignant pleural mesothelioma were enrolled from 13 centres in six countries. Patients received pembrolizumab (10 mg/kg every 2 weeks) for up to 2 years or until confirmed progression or unacceptable toxicity. Key eligibility criteria included measurable disease, failure of standard therapy, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1. PD-L1 positivity was defined as expression in 1% or more of tumour cells by immunohistochemistry. Response was assessed based on investigator review using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST; version 1.1). Primary endpoints were safety and tolerability, analysed in the all-patients-as-treated population, and objective response, analysed for the full-analysis set. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT02054806, and is ongoing but not recruiting participants.
Findings
As of June 20, 2016, 25 patients received pembrolizumab. 16 (64%) patients reported a treatment-related adverse event; the most common adverse event were fatigue (six [24%]), nausea (six [24%]), and arthralgia (five [20%]). Five (20%) patients reported grade 3 treatment-related adverse events. Three (12%) patients required dose interruption because of immune-related adverse events: one (4%) of 25 each had grade 3 rhabdomyolysis and grade 2 hypothyroidism; grade 3 iridocyclitis, grade 1 erythema multiforme, and grade 3 erythema; and grade 2 infusion-related reaction. No treatment-related deaths or discontinuations occurred. Five (20%) patients had a partial response, for an objective response of 20% (95% CI 6·8–40·7), and 13 (52%) of 25 had stable disease. Responses were durable (median response duration 12·0 months [95% CI 3·7 to not reached]); two patients remained on treatment at data cutoff.
Interpretation
Pembrolizumab appears to be well tolerated and might confer anti-tumour activity in patients with PD-L1-positive malignant pleural mesothelioma. Response durability and efficacy in this patient population warrants further investigation.
Funding
Merck.
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Tumor Treating Fields aanvullend op chemotherapie verbetert de effectiviteit bij patienten met pleurale mesothelioma = asbestkanker en verlengt overall overleving
- Immuuntherapie met nivolumab plus ipilimumab verbetert significant de algehele overleving versus chemotherapie (23 vs 15 procent op 3-jaars meting) bij patiënten met niet operabele mesothelioom van de longen
- Dendritische celtherapie heeft succes bij patienten met mesothelioma - asbestkanker. Erasmus doet oproep dat meer patienten zich aanmelden voor de studie.
- Pembrolizumab, een anti-PD medicijn geeft uitstekende resultaten bij zwaar voorbehandelde patienten met mesothelioma
- Mesothelioma - asbestkanker: Ranpirnase oftewel Onconase geeft een significant verschil in overleving bij mesothelioma
- Mesothelioma: Nieuwe chemotherapie combinaties verlengen de mediane overlevingstijd van patiënten met mesothelioma in longen en buik niet tot nauwelijks
- Mesothelioma - asbestkanker informatie: Alimta en dubbele chemo met als aanvulling B12 en foliumzuur zorgt voor opmerkelijke resultaten bij inoperabele mesothelioma
- mesothelioma - asbestkanker: vorinostat (Zolinza) aanvullend op cisplatin en alimta geeft geen enkel positief effect op overlevingstijd, aldus grote gerandomiseerde fase 3 studie.
- Mesothelioma informatie: longvlieskanker en buikvlieskanker





Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Pembrolizumab, een anti-PD medicijn geeft uitstekende resultaten bij zwaar voorbehandelde patienten met mesothelioma"