Mocht u kanker-actueel de moeite waard vinden en ons willen ondersteunen om kanker-actueel online te houden dan kunt u ons machtigen voor een periodieke donatie via donaties: https://kanker-actueel.nl/NL/donaties.html of doneer al of niet anoniem op - rekeningnummer NL79 RABO 0372931138 t.n.v. Stichting Gezondheid Actueel in Amersfoort. Onze IBANcode is NL79 RABO 0372 9311 38
Elk bedrag is welkom. En we zijn een ANBI instelling dus uw donatie of gift is in principe aftrekbaar voor de belasting. En als donateur kunt u ook korting krijgen bij verschillende bedrijven:
19 oktober 2015: Bron: Arab J Urol. 2015 Sep;13(3):225-30. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 Jul 17
Bij blaaskanker wordt vaak BCG - Bacillus Calmette-Guerin als een vorm van immuuntherapie ingezet. Zie in deze lijst het vele bewijs dat BCG uitstekend werkt bij blaaskanker. Nu heeft een 5-jarige studie bij totaal 88 patiënten uitgewezen dat met name bepaalde DNA mutaties in de P53 en P63 en receptorenexpressie van de Her2/Neu een voorspellende waarde hebben of BCG ook werkelijk minder kans op een recidief en levensverlenging geeft.
In relatie tot het stadium van de ziekte blijkt een overexpressie van P-53 mutatie en Her2 ongunstig, een negatieve expressie van de P63 mutatie daarentegen gunstig.
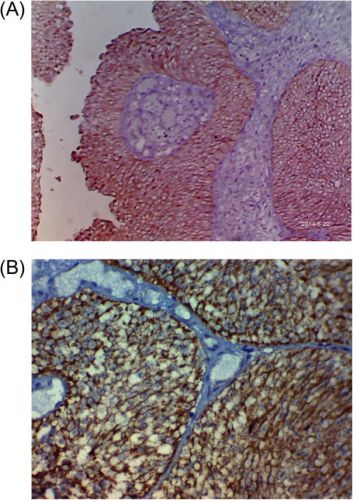
Foto: (A) A case of T1G2, showing a strong membranous reaction to her2/neu; ×100. (B): A case of T1G3, showing a strong membranous reaction to her2/neu; ×200.
Er bleek namelijk een significante relatie tussen overexpressie van de p53 (P = 0.010), her2 (P = 0.025) en negatieve expressie van de p63 (P = 0.025). Er was geen significante relatie tussen een p53 of her2/neu overexpressie en stadium van de ziekte. Echter er was een significante correlatie (P = 0.005) tussen een p63 negatieve expressie en stadium van de tumoren. Er was dus een significante relatie tussen p53 (P = 0.01), her2/neu (P = 0.025) overexpressie en p63 negatieve expressie (P = 0.005) en de kans op een recidief en/of ziekteprogressie.
Conclusie:
De onderzoekers concluderen dat patiënten met transitionele cell carcinoma die geselecteerd waren voor een behandeling met BCG bij voorkeur een positieve expressie van de P63 en een negatieve expressie zouden moeten hebben van P53 en Her2/Neu expressie. Dezxe patiënten bleken minder vatbaar voor een recidief of een progressie van de ziekte na een behandeling met BCG.
Het volledige studieverslag: The prognostic significance of p53, p63 and her2 expression in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer in relation to treatment with bacille Calmette-Guerin is gratis in te zien.
Ook dit studierapport is wellicht interessant: New and contemporary markers of prognosis in nonmuscle invasive urothelial cancer
Hier het abstract van de studie zoals hierboven beschreven:
Patients with transitional cell carcinoma who are selected for BCG treatment should preferably be positively immunoreactive for p63, but negative for both p53 and her2/neu. These patients were less susceptible to recurrence and/or progression after BCG adjuvant therapy.
The prognostic significance of p53, p63 and her2 expression in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer in relation to treatment with bacille Calmette-Guerin.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To investigate whether the immunohistochemical expression of p53, p63 and her2/neu is correlated with the prognosis of tumour recurrence and progression in patients with non-muscle invasive (NMI) bladder cancer.
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
In all, 88 patients diagnosed with NMI transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder in a Urology Department from May 2009 to April 2014 were included in the study. Paraffin-embedded specimens were obtained by transurethral resection of the bladder tumours. Sections on haematoxylin and eosin-stained slides were examined histologically and tumour grade was classified according to the World Health Organisation system (2004) Mostofi classification. The sections were evaluated using p63, p53 and her2/neu immunohistochemical staining before and after immunotherapy with bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG), and patients were followed up for 36 months in the Urology Department.
RESULTS:
For tumour grade there was a significant relationship with the overexpression of p53 (P = 0.010), her2 (P = 0.025) and negativity of p63 (P = 0.025). There was no significant relationship between p53 or her2/neu overexpression and tumour stage. However, there was a significant correlation (P = 0.005) between p63 negativity and tumour stage. There was a significant relationship between p53 (P = 0.01), her2/neu (P = 0.025) overexpression and p63 negativity (P = 0.005) and tumour recurrence and progression.
CONCLUSION:
Patients with transitional cell carcinoma who are selected for BCG treatment should preferably be positively immunoreactive for p63, but negative for both p53 and her2/neu. These patients were less susceptible to recurrence and/or progression after BCG adjuvant therapy. Further studies are needed to investigate the relationship between these three markers and treatment with anti-her2/neu therapies.
KEYWORDS:
BCG; Bladder cancer; Cis, carcinoma in situ; H&E, haematoxylin and eosin; NMI, non-muscle invasive; P53, P63, Her2; TURBT, transurethral resection of the bladder tumour
- PMID:
- 26413353
- PMCID:
- PMC4563013
-
References
1. Oosterlinck W., Lobel B., Jakse G., Malmstrom P.-U., Stockle M., Sternberg C. European Association of Urology; Arnhem: 2003. Guidelines on Bladder Cancer.2. Hall M.C., Chang S.S., Dalbagni G., Seigne J.D., Skinner E.C. The Bladder Cancer Clinical Guideline Update Panel. Guideline for the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer (stages Ta, T1, and Tis) J Urol. 2007;2007(178):2314–2330. Update. [PubMed]3. Cormio L., Tolve I., Annese P., Saracino A., Zamparese R., Sanguedolce F. Altered p53 and pRb expression is predictive of response to BCG treatment in T1G3 bladder cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:4201–4204. [PubMed]4. Nakopoulou L., Vourlakou C., Zervas A., Tzonou A., Gakiopoulou H., Dimopoulos M.A. The prevalence of bcl-2, 53, and Ki-67 immunoreactivity in transitional cell bladder carcinoma and their clinicopathologic correlates. Hum Pathol. 1998;29:146–154. [PubMed]5. Popov Z., Hoznek A., Colombel M., Bastuji-Garin S., Lefrere-Belda M.A., Bellot J. The prognostic value of p53 nuclear overexpression and MIB-1 as a proliferative marker in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer. 1997;80:1472–1481. [PubMed]6. Ovesen H., Horn T., Steven K. Long-term efficacy of intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guerin for carcinoma in situ: relationship of progression to histological response and p53 nuclear accumulation. J Urol. 1997;157:1655–1659. [PubMed]7. Lebret T., Becette V., Barbagelatta M., Herve J.M., Gaudez F., Barre P. Correlation between p53 over expression and response to Bacillus Calmette–Guerin therapy in a high risk select population of patients with T1G3 bladder cancer. J Urol. 1998;159:788–791. [PubMed]8. Zlotta A.R., Noel J.C., Fayt I., Drowart A., Van Vooren J.P., Huygen K. Correlation and prognostic significance of p53, 21WAF1/CIP1and Ki-67 expressions in patients with non muscle invasive bladder tumors treated with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin intravesical therapy. J Urol. 1999;161:792–798. [PubMed]9. Pages F., Flam T.A., Vieillefond A., Abeille X., Lazar V. P53 status does not predict initial clinical response to Bacillus Calmette–Guerin intravesical therapy in T1 bladder tumors. J Urol. 1998;159:1079–1084. [PubMed]10. Yang A., Schweitzer R., Sun D., Kaghad M., Walker N., Bronson R.T. P63 is essential for regenerative proliferation in limb, craniofacial, and epithelial development. Nature. 1999;398:714–718. [PubMed]11. Urist M.J., Di Como C.J., Lu M.L., Charytonowicz E., Verbel D., Crum C.P. Loss of p63 expression is associated with tumor progression in bladder cancer. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:1199–1206. [PubMed]12. Park B.J., Lee S.J., Kim J.I., Lee S.J., Lee C.H., Chang S.G. Frequent alteration of p63 expression in human primary bladder carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2000;60:3370–3374. [PubMed]13. Koga F., Kawakami S., Kumagai J., Takizawa T., Ando N., Arai G. Impaired DeltaNp63 expression associates with reduced beta-catenin. An aggressive phenotype of urothelial neoplasms. Br J Cancer. 2003;88:740–747. [PubMed]14. Matsubara H., Yamada Y., Naruse K., Nakamura K., Aoki S., Taki T. Potential for HER-2/neu molecular targeted therapy for invasive bladder carcinoma comparative study of immunohistochemistry and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:57–63. [PubMed]15. Naruse K., Yamada Y., Nakamura K., Aoki S., Taki T., Zennami K. Potential of molecular targeted therapy of HER-2 and Cox-2 for invasive transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Oncology Rep. 2010;23:1577–1583. [PubMed]16. Olsson H., Fyhr I.M., Hultman P., Jahnson S. HER2 status in primary stage T1 urothelial cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2012;46:102–107. [PubMed]17. Simonetti S., Russo R., Ciancia G., Altieri V., De Rosa G., Insabato L. Role of polysomy 17 in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: immunohistochemical study of HER2/neu expression and fish analysis of c-erbB-2 gene and chromosome 17. Int J Surg Pathol. 2009;17:198–205. [PubMed]18. Skagias L., Politi E., Karameris A., Sambaziotis D., Archondakis A., Vasou O. Prognostic impact of HER2/neu protein in urothelial bladder cancer. Survival analysis of 80 cases and an overview of almost 20 years’ research. J BUON. 2009;14:457–462. [PubMed]19. Eble J.N., Sauter G., Epstein J.I., Sesterhenn I.A. IARC; Lyon: 2004. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs.20. Sobin L.H., Gospodarowicz M.K., Wittekind C. 7th ed. Wiley; Weinheim: 2009. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours.21. Herr H.W., Laudone V.P., Badalament R.A., Oettgen H.F., Pramod C.S., Freedman B.D. Bacillus Calmette–Guerin therapy alters the progression of non muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1988;6:1450–1455. [PubMed]22. Saint F., Le Frere Belda M., Quintela R., Hoznek A., Patard J.J., Bellot J. Retreatment p53 nuclear overexpression as a prognostic marker in superficial bladder cancer treated with bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) Eur Urol. 2004;45:475–482. [PubMed]23. Lacombe L., Dalbagni G., Zhang Z.F., Cordon-Cardo C., Fair W.R., Her H.W. Overexpression of p53 protein in a high-risk population of patients with non muscle invasive bladder cancer before and after Bacillus Calmette–Guerin therapy: correlation to clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:2646–2652. [PubMed]24. Nishizaki M., Fujiwara T., Tanida T., Hizuta A., Nishimori H., Tokino T. Recombinant adenovirus expressing wild-type p53 is antiangiogenic: a proposed mechanisms for bystander effect. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:1015–1023. [PubMed]25. Pfister C., Flaman J.M., Dunet F., Grise P., Frebourg T. P53 mutations in bladder tumors inactivate the transactivation of the P21 and BAX genes, and have a predictive value for the clinical outcome after Bacillus Calmette–Guerin. J Urol. 1999;162:69–73. [PubMed]26. Ick K., Schultz M., Stout P., Fan K. Significance of p53 overexpression in urinary bladder transitional cell carcinoma in situ before and after Bacillus Calmette–Guerin treatment. Urology. 1997;49:541–547. [PubMed]27. Di Como C.J., Urist M.J., Babayan I., Drobnjak M., Hedvat C.V., Teruya-Feldstein J. P63 expression profiles in human normal and tumor tissues. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:494–501. [PubMed]28. Yang A., Kaghad M., Wang Y., Gillett E., Fleming M.D., Dötsch V. P63, a p53 homolog at 3q27–29, encodes multiple products with transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol Cell. 1998;2:305–316. [PubMed]29. Morgan B.E., Salup R., Morgan M.B. Differential C-erbB-2 and VEGF expression following BCG immunotherapy in non muscle invasive papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urol Oncol. 2002;7:67–72. [PubMed]30. Alexai A., Badercai F., Zahoi D., Lighezani R., Izvernariui D., Raicai M. Clinical significance of Her2/neu overexpression in urothelial carcinomas. Romanian J Morph Embryol. 2010;51:277–282. [PubMed]31. Charfia S., Khabir A., Mnifa H., Ellouzea S., Mhirib M., Sellamia T. Immunohistochemical expression of HER2 in urothelial bladder carcinoma and its correlation with p53 and p63 expression. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2013;1:17–21.
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Immuuntherapie met BCG wordt om succesvol te zijn bepaald door enkele belangrijke DNA mutaties p53, p63 en her2 expressie
- Drie jaar lang een volledige dosis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) is de best mogelijke behandeling met de beste resultaten op ziektevrije tijd en overall overleving voor patiënten met matig tot hoog risico van niet spier invasieve blaaskanker - NMIBC
- BCG - Bacillus Calmette-Guerin: Hier een mini overzicht gepubliceerd van wetenschappelijke studies en bewijzen over het gebruik van BCG - Bacillus Calmette-Guerin - als succesvolle immuuntherapie bij blaaskanker.
- BCG - Bacillus Calmette-Guerin geeft significant betere kans op definitieve genezing van blaaskanker dan Epirubicine plus Interferon-Alpha2b voor zowel primaire blaaskanker, als secondaire vorm van blaaskanker als recidief van blaaskanker
- BCG - Bacillus Calmette-Guerin in een lage dosis - 27 mg. geeft een nagenoeg zelfde therapeutische resultaat bij tegengaan van recidief of remming van blaaskanker dan de standaard dosis van 81 mg. blijkt uit 10-jarige gerandomiseerde studie.
- BCG - Bacillus Calmette Guerin werkt effectiever als patient eerst geopereerd wordt en tumorvrij is bij aanvang van BCG behandeling.
- BCG - Bacillus Calmette-Guerin bij blaaskanker: Hier een mini overzicht gepubliceerd van wetenschappelijke studies en bewijzen over het gebruik van BCG - Bacillus Calmette-Gue´rin - als succesvolle immuuntherapie bij blaaskanker. Update 23 februari 2010



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Immuuntherapie met BCG wordt om succesvol te zijn bepaald door enkele belangrijke DNA mutaties p53, p63 en her2 expressie"