Zie ook literatuurlijst niet-toxische middelen, voeding en weinig belastende behandelingen specifiek bij borstkanker van arts-bioloog drs. Engelbert Valstar
13 augustus 2021: Nieuwe gegevens uit de MONALEESA-3 studie na een follow-up van eerdere studieresultaten laat zien dat fulvestrant en ribociclib (een zogeheten CDK4/6 remmer) samen een verbetering geeft van 10% in de overall overleving in vergelijking met een placebo, ondanks het feit dat het meerendeel van de borstkankerpatiënten meerdere andere behandelingen hebben gehad voordat ze aan deze behandeling begonnen. Na 5 jaar waren er minder recidieven of progressie van de ziekte met een verbetering van 15% in de totale overleving.
Bij de borstkankerpatiënten die deze behandeling als eerstelijns kregen is de mediane overleving nog niet eens bereikt voor fulvestrant en ribociclib in vergelijking met placebo en fulvestrant bij de patiënten die het in de eerste lijn kregen.
En in de tweede lijns behandeling was er nog steeds een voordeel van ongeveer 6 maanden bij deze patiënten, in termen van algehele overleving, die ribociclib in combinatie met fulvestrant als tweedelijnstherapie kregen.
Vergelijkbare resultaten werden gezien met palbociclib plus fulvestrant in de PALOMA-3 studie, dat nu rfesultaten heeft van een lange follow-up na 73 maanden. Uit de nieuwste gegevens was een verbetering van 20% in de totale overleving met een verbetering van mediaan ongeveer 6 maanden in de totale overleving van 28 tot 35 maanden in deze patiënten die eerder waren behandeld met hormoontherapie en in veel gevallen ook met chemotherapie.
Deze twee studies benadrukken dat het gebruik van CDK4/6-remmers vooral ook in de eerstelijns moet plaats vinden.
30 juni 2020: lees ook dit artikel: https://kanker-actueel.nl/NL/circulerend-tumor-dna-in-bloed-bij-start-van-behandeling-met-fulvestrant-met-of-zonder-palbociclib-geeft-aanwijzingen-voor-prognose-op-aanslaan-van-de-behandeling-bij-patienten-met-uitgezaaide-borstkanker.html
30 juli 2019: ook de uitkomsten van toevoeging van palbociclib in de praktijk loopt gelijk met de uitkomsten uit de klinische trials ondanks meer lagere doseringen blijkt uit een nieuwe studie: Progression-Free Survival for Real-World Use of Palbociclib in Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer
Uit het abstract:
Results
Seventy patients were included in the final analysis. Median PFS was 26.4 months. No significant differences in PFS were observed between final doses of palbociclib (p=0.77). Time to first dose reduction was 2.3 months. Median TTF was 26.1 months. Dose delays, reductions, and grade 3-4 neutropenia were common (63%, 57%, and 62%).
Conclusions
Real-world first-line palbociclib produced outcomes similar to PALOMA-2 (median PFS 26.4 months vs 24.8 months) despite more dose reductions (57% vs 36%) and shorter time to first dose reduction (2.3 vs 3.0 months). No significant differences in PFS were observed for the varying palbociclib doses. Palbociclib dose reductions may not significantly affect PFS in the first-line setting.
4 mei 2018: Lees ook dit artikel: zowel ribociclib als palbociclib worden inmiddels vergoed vanuit de basisverzekering.
5 februari 2015: Bron FDA
De FDA heeft nu ook officieel goedkeuring gegeven aan palbociclib naast femara / letrozole voor hormoongevoelige borstkanker (ER positief en Her2 negatief. Zie onderstaande studiepublicatie. FDA goedkeuring staat onderaan artikel.
15 oktober 2014: De FDA heeft het zogeheten priority review gegeven aan de studie naar palbociclib naast femara - letrozole in de eerste lijnsbehandeling. Dit is zo ontzettend belangrijk dat snel resultaten bekend worden voor al die nieuwe klasse van medicijnen gericht op receptorenexpressie en DNA mutaties, zie ook hieronder 1e studiepublicatie met palbolicidib met hele hele goede resultaten.
Het Amerikaanse studieprotocol staat hier: Expanded Access Study Of Palbociclib (PD-0332991) In Combination With Letrozole As Treatment Of Post-Menopausal Women With HR-Positive, Her2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer For Whom Letrozole Therapy Is Deemed Appropriate
13 mei 2014: Bron: 1. Finn RS, et al: American Association for Cancer Research ( AACR ) Annual Meeting 2014 in San Diego
Palbociclib, gegeven naast letrozole - femara verdubbelt ziektevrije tijd van 10,2 maanden naar 20,2 maanden (P = .0004).als eerste lijns behandeling bij borstkankerpatiënten met voornamelijk hormoongevoelige vorm van borstkanker (ER positief en Her2 negatieve receptoren status).
Patiënten die in de studie werden opgenomen hadden ziekteprogressie of een recidief gekregen of hadden uitzaaiingen in andere organen en/of botten.
Deze resultaten zijn de eerste resultaten uit de gerandomiseerde fase II PALOMA 1 studie. Twee gescheiden studies met resp. 66 borstkankerpatiënten en 99 borstkankerpatiënten zijn in deze tussenevaluatie betrokken en opgeteld in de resultaten. Dit werd bekendgemaakt op het AACR congres in San diego afgelopen maand.
Uit de studie blijkt ook dat met name twee biomarkers / een receptor CCND1 en een gen p16, een grote rol spelen in het succes van deze medicijnen combinatie van Palbociclib en letrozole - femara. Maar volgens de onderzoekers blijft de ER positieve status nog wel de belangrijkste indicator voor het succes van de medcijnen. Palbociclib is een zogeheten first-in-class cyclin-dependent kinaseremmer ook wel CDK4 en CDK6 remmers genoemd.
Deze resultaten zijn echt spectaculair te noemen, ook omdat de studie werd uitgevoerd bij vrouwen na de eerste diagnose en als eerste lijns behandeling en superieur zijn aan de nu geldende behandeling.
Dennis Slamon, MD, PhD, Professor of Medicine and Director of the Revlon/UCLA Women’s Cancer Program, studieleider van de PALOMA studies zegt: "De impact van deze studie kan enorm zijn. We doen verder onderzoek in een fase III studie (PALOMA - 2) met deze medicijnen combinatie, maar de recente gegevens zijn net zo opwindend en spectaculair dan de eerste studies waren met trastuzumab ( Herceptin ) voor
HER2 - positieve borstkanker ."
Palbociclib is door de FDA als "Breakthrough Therapy" bestempeld en toestemming verleend om te gebruiken als eerstelijns behandeling van oestrogeen receptor - positieve (ER-pos.) en HER2 - negatieve gevorderde borstkanker."
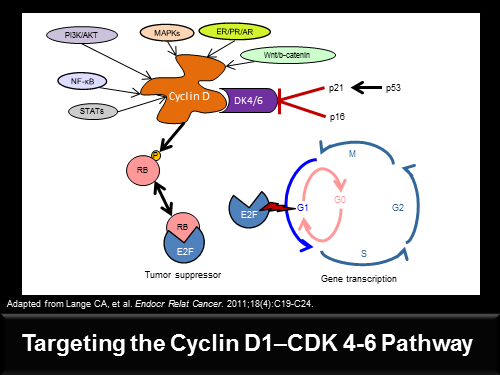
Studieresultaten:
De fase II studie (PALOMA 1) bestaat uit twee gescheiden studies.
In deel 1 werden gerandomiseerd (willekeurig) 66 vrouwen opgenomen in de leeftijd na de overgang (postmenopauzaal) met oestrogeenreceptor - positieve + HER2 - negatieve, lokaal recidiverende of uitgezaaide borstkanker. Als behandeling werd de vrouwen de combinatie van palbociclib plus letrozol - femara of letrozole - femara alleen gegeven.
In deel 2 werden nog eens 99 patiënten gerandomiseerd ingedeeld dezelfde behandeling gegeven als in deel 1. Ook deze patiënten hadden dezelfde kenmerken als in deel 1 (ER-pos + HER2-neg) maar bij deze 99 vrouwen waren bij twee extra potentiële biomarkers afwijkingen geconstateerd: overexpressie bij receptor CCND1 en / of verlies van p16.
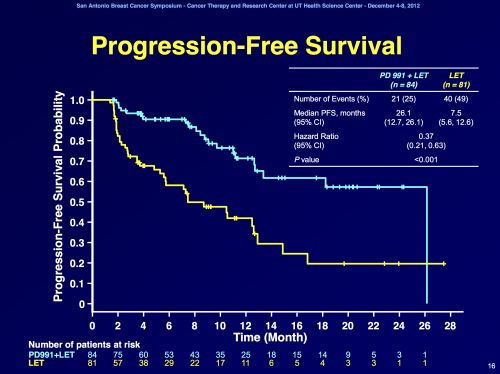
Bij de vrouwen in deel 1 bleek de progressie-vrije overleving 26,1 maanden voor de combinatie van palbociclib plus letrozol versus 5,7 maanden voor letrozol alleen ( P < .0001 ). Een verlenging dus met 20 maanden voor een klinisch kankervrije situatie.
In deel 2 bleek de progressie-vrije overleving 18,1 maanden (voor palbocibib plus letrozole - femara) versus 11 maanden (femara - letrozole alleen) te zijn ( p = 0,0046 ).
Richard S. Finn, MD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, presentator van de studie op het AACR congres merkt op dat de vrouwen met een overexpressie van CCND1 en verlies van p16 functie anders reageerden op de medicijnencombinatie dan op letrozle - femara alleen.
Dr. Finn: "Overall blijft de boodschap van deze studie dat oestrogeen receptor positiviteit nog wel de meest gevoelige voorspeller van een reactie op dit nieuwe medicijn blijft in combinatie met letrozol - femara."
Beste totale respons was 43% voor de combinatie versus 33 % voor letrozol alleen. Klinisch voordeel (volledige en gedeeltelijke remissie plus stabiele ziekte ) was 81 % versus 58 % , respectievelijk. Subgroep analyses toonden aan dat de progressie-vrije overleving voor de combinatie in alle subgroepen gold onafhankelijk van leeftijd, plaatsen van de uitzaaiingen - gemetastaseerde ziekte en eerdere adjuvante behandelingen of geen eerdere adjuvante therapie.
Overall survival na eerste diagnose was 37,5 maanden voor de combinatie palbociclib plus letrozol - femara versus 33,3 maanden met letrozol alleen. Dit verschil was op moment van opmaken van de resultaten nog niet statistisch significant.
Bijwerkingen alleszins aanbaardbaar:
De toxiciteit van palbociclib in combinatie met letrozol was aanvaardbaar. Enkele bijwerkingen kwamen wel vaker voor met de combinatie palbociclib plus letrozol - femara dan met letrozol - femara alleen waaronder neutropenie ( graad 3 , 48 % , graad 4 , 6 % ) , leukopenie ( graad 3 , 19 % ) , vermoeidheid en bloedarmoede. Maar alle bijwerkingen waren goede behandelbaar
Aan het einde van de studie was 23 % van de patiënten behandeld met palbociclib plus letrozol - femara nog steeds in behandeling versus 10 % op letrozol - femara alleen. De meest voorkomende reden voor het staken van de behandeling was progressie van de ziekte..
Conclusie:
"Deze gegevens met palbociclib plus letrozol zijn indrukwekkend goed en indien deze worden bevestigd in een grotere fase III studie, zal deze aanpak een extra alternatief betekenen voor borstkankerpatiënten met receptor - positieve gemetastaseerde ziekte vergelijkbaar met de resultaten die eerdere studies met everolimus en letrozol - femara lieten zien", aldus de onderzoekers.
Richard S. Finn, MD heeft gemeld geen potentiële belangenconflicten te hebben. Dr Slamon heeft honoraria ontvangen van Genentech en Sanofi - Aventis.
Het volledige studierapport: Final results of a randomized Phase II study of PD 0332991, a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-4/6 inhibitor, in combination with letrozole vs letrozole alone for first-line treatment of ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1; TRIO-18) is nog niet beschikbaar maar op clinical trials.gov kunt u dus wel het studieprotocol inzien.
Op de website van Pfizer, de producent van Palbociclib, staat een artikel over goedkeuring van FDA als doorbraak medicijn
Wellciht ook goed om te lezen naast bovenstaand artikel: https://kanker-actueel.nl/NL/studiepublicaties-van-niet-toxische-middelen-en-behandelingen-uit-literatuurlijst-van-arts-bioloog-drs-engelbert-valstar-gerelateerd-aan-borstkanker.html
Hier het abstract zoals dat op het AACR werd gepresenteerd en waaruit ik bovenstaand artikel heb gecomponeerd:
Final results of a randomized Phase II study of PD 0332991, a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-4/6 inhibitor, in combination with letrozole vs letrozole alone for first-line treatment of ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1; TRIO-18)
| Presentation Time: | Sunday, Apr 06, 2014, 10:15 AM -10:35 AM |
| Location: | Hall F-G, San Diego Convention Center |
| Author Block: | Richard S. Finn, John P. Crown, Istvan Lang, Katalin Boer, Igor M. Bondarenko, Sergey O. Kulyk, Johannes Ettl,Ravindranath Patel, Tamas Pinter, Marcus Schmidt, Yaroslav V. Shparyk, Anu R. Thummala, Nataliya L. Voytko,Xin Huang, Sindy T. Kim, Sophia S. Randolph, Dennis J. Slamon. UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, Irish Cooperative Oncology Research Group, Dublin, Ireland, Orszagos Onkologiai Intezet, Budapest, Hungary, Onkologia, Szent Margit Korhaz, Budapest, Hungary, Dnipropetrovsk City Multiple-Discipline Clinical Hospital, Dnipropetrovsk, Ukraine, Donetsk City Oncology Dispensary, Donetsk, Ukraine, Klinikum rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany, Comprehensive Blood and Cancer Center, Bakersfield, CA, Petz Aladar Teaching Hospital Győr, Győr, Hungary, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University Mainz, Mainz, Germany, Lviv State Oncologic Regional Treatment and Diagnostic Center, Ukraine, Lviv, Ukraine, Comprehensive Cancer Centers of Nevada, Henderson, NV, Kyiv City Clinical Oncology Center, Kyiv, Ukraine, Pfizer Oncology, San Diego, CA, University of California, Los Angeles, CA |
| Abstract Body: | Background: PD 0332991 (palbociclib), a selective inhibitor of CDK-4/6, prevents DNA synthesis by blocking cell cycle progression. Preclinical studies identified luminal ER+ breast cancer cell lines with elevated expression of cyclin-D1, Rb and reduced p16 expression as being associated with palbociclib sensitivity (Finn et al. 2009). In addition, synergistic activity was seen in vitro when combined with tamoxifen. As a result of these data Phase Ib safety testing was performed, and led to this randomized Phase II study using a recommended Phase II dose of palbociclib (P) 125 mg QD for 3 weeks followed by 1 week off plus letrozole (L) 2.5 mg QD continuously. Methods: This Phase II trial was designed as a two-part study evaluating P+L in front-line ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer (MBC). Part 1 enrolled post-menopausal patients (pts) with this subtype using ER+/HER2- biomarkers while Part 2 enrolled pts with the same MBC subtype additionally screened for CCND1 amplification and/or loss of p16. The primary endpoint was investigator assessed progression-free survival (PFS) defined as time from randomization to objective progression or death. Secondary endpoints included objective response rate, overall survival, safety, and correlative biomarker studies. In both parts, post-menopausal women with ER+/HER2- MBC were randomized 1:1 to receive either P+L or L alone. Pts continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or consent withdrawal and were followed for tumor assessments every 2 months. The trial had 80% power to detect a 50% improvement in median PFS (hazard ratio 0.67 [P+L vs. L] with a 1-sided alpha=0.10). Results: A total of 165 pts were randomized in this Phase II study; 66 pts in Part 1 and 99 pts in Part 2. Baseline characteristics were balanced between treatment arms. The final analysis of primary endpoint showed a statistically significant improvement in PFS for the P+L arm (20.2 months) vs. L arm (10.2 months) with hazard ratio (HR)=0.488 (95% CI: 0.319, 0.748) and 1-sided p=0.0004. The treatment effects were also demonstrated when Part 1 and Part 2 were analyzed separately (HR=0.299 [95% CI: 0.156, 0.572]; 1-sided p=0.0001 for Part 1 and HR=0.508 [95% CI: 0.303, 0.853]; 1-sided p=0.0046 for Part 2). The OS analysis with 61 events demonstrated a trend in favor of P+L vs. L (37.5 months vs. 33.3 months, respectively; HR=0.813; p=0.2105). The most common adverse events in the P+L arm were neutropenia, leukopenia, fatigue, and anemia. Conclusions: P+L demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS and showed significant clinical benefit as first-line treatment of ER+/HER2- advanced BC. A Phase III study of P+L in this same MBC population is ongoing. |
FDA Approves Palbociclib - Ibrance in Combination With Letrozole for Advanced Breast Cancer
FDA approves Ibrance for postmenopausal women with advanced breast cancer
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today granted accelerated approval to Ibrance (palbociclib) to treat advanced (metastatic) breast cancer.
Breast cancer in women is the second most common type of cancer in the United States. It forms in the breast tissue and in advanced cases, spreads to surrounding normal tissue. The National Cancer Institute estimates that 232,670 American women were diagnosed with breast cancer and 40,000 died from the disease in 2014.
Ibrance works by inhibiting molecules, known as cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) 4 and 6, involved in promoting the growth of cancer cells. Ibrance is intended for postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative metastatic breast cancer who have not yet received an endocrine-based therapy. It is to be used in combination with letrozole, another FDA-approved product used to treat certain kinds of breast cancer in postmenopausal women.
“The addition of palbociclib to letrozole provides a novel treatment option to women diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer,” said Richard Pazdur, M.D., director of the Office of Hematology and Oncology Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “The FDA is committed to expediting marketing approval of cancer drugs through our accelerated approval regulations.”
The FDA granted Ibrance breakthrough therapy designation because the sponsor demonstrated through preliminary clinical evidence that the drug may offer a substantial improvement over available therapies. It also received a priority review, which provides for an expedited review of drugs intended to provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness in the treatment of a serious condition or meet an unmet medical need. Ibrance is being approved more than two months ahead of the prescription drug user fee goal date of April 13, 2015, the date when the agency was scheduled to complete its review of the application.
Ibrance is being approved under the FDA’s accelerated approval program, which allows approval of a drug to treat a serious or life-threatening disease based on clinical data showing the drug has an effect on a surrogate endpoint reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit to patients. This program provides earlier patient access to promising new drugs while the company conducts confirmatory clinical trials.
The drug’s efficacy was demonstrated in 165 postmenopausal women with ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who had not received previous treatment for advanced disease. Clinical study participants were randomly assigned to receive Ibrance in combination with letrozole or letrozole alone. Participants treated with Ibrance plus letrozole lived about 20.2 months without their disease progressing (progression-free survival), compared to about 10.2 months seen in participants receiving only letrozole. Information on overall survival is not available at this time.
The most common side effects of the drug were a decrease in infection-fighting white blood cells called neutrophils (neutropenia), low levels of white blood cells (leukopenia), fatigue, low red blood cell counts (anemia), upper respiratory infection, nausea, inflammation of the lining of the mouth (stomatitis), hair loss (alopecia), diarrhea, low blood platelet counts (thrombocytopenia), decreased appetite, vomiting, lack of energy and strength (asthenia), damage to the peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathy) and nosebleed (epistaxis). Healthcare professionals should inform patients of these risks.
It is recommended that treatment begin with a 125 milligram dose for 21 days, followed by seven days without treatment. Healthcare professionals are advised to monitor complete blood count prior to start of therapy and at the beginning of each cycle, as well as on Day 14 of the first two cycles, and as clinically indicated.
Ibrance is marketed by New York City-based Pfizer, Inc.
The FDA, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, promotes and protects the public health by, among other things, assuring the safety, effectiveness, and security of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products for human use, and medical devices. The agency also is responsible for the safety and security of our nation’s food supply, cosmetics, dietary supplements, products that give off electronic radiation, and for regulating tobacco products.
Clinical Trial Results
The approval was based on the results of a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial in 165 postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor–positive, HER2-negative, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who had not received previous systemic treatment for advanced disease. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either palbociclib (125 mg/d for 21 days, followed by 7 days off treatment) plus letrozole (2.5 mg/d continuously throughout the 28-day cycle) or letrozole alone.
Among the 165 patients, 43% had received chemotherapy and 33% had received antihormonal therapy as a neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment; 49% of patients had no prior systemic therapy in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting. The majority of patients (98%) had metastatic disease.
Participants treated with palbociclib plus letrozole had a median progression-free survival of 20.2 months (95% confidence interval = 13.8–27.5), compared to about 10.2 months (95% CI = 5.7–12.6) in patients receiving only letrozole (hazard ratio = 0.488, 95% CI = 0.319–0.748). The treatment effect of the combination on progression-free survival was also supported by a retrospective radiographic independent review (HR = 0.621, 95% CI = 0.378–1.109). The overall response rate in patients with measurable disease was higher in the palbociclib-plus-letrozole arm compared to the letrozole-alone arm (55.4% vs 39.4%). Information on overall survival is not available at this time.
The most common side effects of the drug were neutropenia, leukopenia, fatigue, anemia, upper respiratory infection, nausea, stomatitis, alopecia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, decreased appetite, vomiting, asthenia, peripheral neuropathy, and pistaxis. The most frequently reported serious adverse reactions in patients receiving the combination were pulmonary embolism (4%) and diarrhea (2%). Health-care professionals should inform patients of these risks.
It is recommended that treatment begin with a 125 mg dose for 21 days, followed by 7 days without treatment. Health-care professionals are advised to monitor complete blood count prior to start of therapy and at the beginning of each cycle, as well as on day 14 of the first two cycles, and as clinically indicated.
Approval History
The FDA granted palbociclib Breakthrough Therapy designation in April 2013 based on preliminary evidence of clinical activity in this patient population. It also received a priority review, which provides for an expedited review of drugs intended to provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness in the treatment of a serious condition or meet an unmet medical need. Palbociclib is being approved more than 2 months ahead of the prescription drug user fee goal date of April 13, 2015.
This accelerated approval is based on demonstration of an improvement in progression-free survival. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in an ongoing confirmatory trial.
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Mutaties in ESR1- en PIK3-pathway-genen gemeten via ctDNA bij vrouwen met borstkanker met ER+ en Her2-neg blijken ook bij ziekteprogressie na palbociclib in bloed voor te komen copy 1
- fulvestrant plus palbociclib geeft betere ziekteprogressievrije overleving - 33 versus 30 maanden - dan letrozole (femara) plus palbociclib maar is geen statistisch significant verschil copy 1 copy 1
- Palbociclib heeft geen statistisch significant effect op overall overleving voor patienten met groot risico op recidief van invasieve HR-positieve en HER2-negatieve borstkanker
- Neutropenie - te weinig witte bloedlichaampjes - blijkt voorspellende factor van effectiviteit van palbociclib bij verschillende vormen van kanker met solide tumoren, waaronder borstkanker
- Palbociclib (CDK4/6 remmer) + letrozole - femara verdubbelt ziektevrije tijd van 10 vs 20 maanden als eerstelijns behandeling bij borstkankerpatiënten met borstkanker ER pos. en Her2 neg. status
- Palbociclib plus fulvestrand geeft langere overall overleving en progressievrije ziekte dan alleen fulvesrtrand bij hormoonresistente borstkanker copy 1
- Palbociclib, gegeven naast letrozole - femara verdubbelt ziektevrije tijd bij borstkanker ER-pos en Her2-neg
- Palbociclib geeft samen met andere medicijnen zoals fulvestrand en femara uitstekende resultaten bij hormoongevoelige borstkanker. Hier enkele artikelen:



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Palbociclib (CDK4/6 remmer) + letrozole - femara verdubbelt ziektevrije tijd van 10 vs 20 maanden als eerstelijns behandeling bij borstkankerpatiënten met borstkanker ER pos. en Her2 neg. status"