Abstract
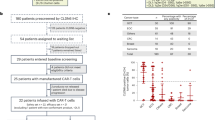
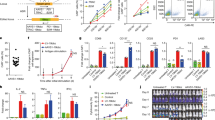
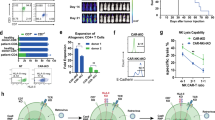
In a phase 1 clinical trial open to accrual from 2004 to 2009, we treated children with neuroblastoma with Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-specific T lymphocytes and CD3-activated T cells—each expressing chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) targeting GD2 but without an embedded co-stimulatory sequence (first-generation CARs). These CARs incorporated barcoded sequences to track each infused population. We previously reported outcomes up to 5 years and now report long-term outcomes up to 18 years. Of 11 patients with active disease at infusion, three achieved a complete response that was sustained in two patients, one for 8 years until lost to follow-up and one for more than 18 years. Of eight patients with no evidence of disease at the time of CAR-T administration, five are disease free at their last follow-up between 10 years and 15 years after infusion. Intermittent low levels of transgene were detected during the follow-up period with significantly greater persistence in those who were long-term survivors. Despite using first-generation vectors that are no longer employed because of the lack of co-stimulatory domains, patients with relapsed/refractory neuroblastoma achieved long-term disease control after receiving GD2 CAR-T cell therapy, including one patient now in remission of relapsed disease for more than 18 years.
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00085930.



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "CAR-T celtherapie maakt dat kinderen met neuroblastoma nu in 2025 al meer dan 10 jaar kankervrij zijn. Met uitgelicht een prachtig overlevingsverhaal van een kind van 4 jaar die anno 2025 al 19 jaar kankervrij is."