16 augustus 2015: U kunt het volledige studierapport: Randomized Phase II Trial of All-Trans-Retinoic Acid With Chemotherapy Based on Paclitaxel and Cisplatin As First-Line Treatment in Patients With Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer gratis inzien.
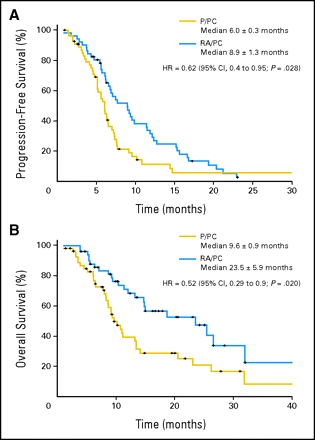
Met een hele duidelijke verbetering van de ziektevrije tijd en vermindering van de bijwerkingen. Hoe zou dat uitpakken zonder chemo denk ik dan? Of met arseentrioxide (ATO), zoals bij leukemie heel goed uitpakt. Hier de grafiek bij longkanker naast chemo:
Maar lees ook eens dit studierapport: Vitamin A, Cancer Treatment and Prevention: The New Role of Cellular Retinol Binding Proteins over de rol van vitamine A in het ontstaan en/of preventie van kanker. Bijzonder interessant voor artsen en wetenschappers denk ik. Abstract van deze studie staat ook onderaan artikel.
10 december 2012:
All-trans-retinoic acid ( ATRA) en arseentrioxide (ATO) samen zorgt bij APL - Acute Promyelocitische Leukemie voor nagenoeg volledige genezing (98,5%) zonder gebruik te maken van chemo. Het bijzondere aan die studie is dat kankercellen door ATRA worden getransformeerd tot gewone gezonde cellen en niet worden gedood door welk middel dan ook. Lees ook die studie eens, klik hier, en is hoewel alleen nog bewezen bij leukemie toch ook interessant als aanvulling op onderstaand artikel van ATRA bij longkanker.
26 juli 2010: Journal of Clinical Oncology, Vol 28, No 21 (July 20), 2010: pp. 3463-3471
Atra - All-trans-retinoic Acid (een vorm van vitamine A) wordt gegeven naast chemo aan longkankerpatienten met pleurale niet-kleincelliige longkanker (stadium IIIB en IV) dan geeft dat een significant langere ziektevrije tijd en levensduur. Dit blijkt uit een gerandomiseerde fase II studie bij 104 longkankerpatienten waarbij elke groep wel chemo kreeg maar 1 groep een placebo als toevoeging en de andere groep dus de Atra - All-trans-Retinoic Acid. Het verschil in progressievrije tijd bleek significant beter voor de Atra groep: (hazard ratio, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.4 to 0.95). Ook de responserate, het aanslaan van de behandeling verdubbelde in de Atra groep t.o.v. de alleen chemogroep. Overigens wordt Atra - All-trans-retinoic Acid ook veel en succesvol gebruikt voor kinderen met leukemie.
Hier het abstract van de studie:
the combination of ATRA with the standard CT regimen is a safe and potentially useful treatment for NSCLC in terms of response rate (RR) and progression-free survival (PFS)
- © 2010 by American Society of Clinical Oncology
Randomized Phase II Trial of All-Trans-Retinoic Acid With Chemotherapy Based on Paclitaxel and Cisplatin As First-Line Treatment in Patients With Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- Oscar Arrieta,
- Claudia H. González-De la Rosa,
- Elena Aréchaga-Ocampo,
- Geraldine Villanueva-Rodríguez,
- Tania L. Cerón-Lizárraga,
- Luis Martínez-Barrera,
- María E. Vázquez-Manríquez,
- Miguel Ángel Ríos-Trejo,
- Miguel Á. Álvarez-Avitia,
- Norma Hernández-Pedro,
- Carlos Rojas-Marín and
- Jaime De la Garza
+ Author Affiliations
- Corresponding author: Oscar Arrieta, MD, Department of Medical Oncology, Instituto Nacional de Cancerología, San Fernando #22, Col Sección XVI, Tlalpan, 14080 México, DF, México; e-mail: ogar@servidor.unam.mx.
-
Presented in part at the Annual Meeting on Molecular Markers in Cancer of the American Society of Clinical Oncology-National Cancer Institute-European Organisation for the Research and Treatment of Cancer, October 30-November 1, 2008, Hollywood, FL; at the 13th World Conference on Lung Cancer, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, July 31-August 4, 2009, San Francisco, CA; and at the ECCO 15 34th ESMO Multidisciplinary Congress, September 20-24, 2009, Berlin, Germany.
Abstract
Purpose This randomized phase II trial evaluated whether the combination of cisplatin and paclitaxel (PC) plus all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) increases response rate (RR) and progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with an acceptable toxicity profile and its association with the expression of retinoic acid receptor beta 2 (RAR-β2) as a response biomarker.
Patients and Methods Patients with stages IIIB with pleural effusion and IV NSCLC were included to receive PC, and randomly assigned to receive ATRA 20 mg/m2/d (RA/PC) or placebo (P/PC) 1 week before treatment until two cycles were completed. RAR-β2 expression was analyzed in tumor and adjacent lung tissue.
Results One hundred seven patients were included, 55 in the P/PC group and 52 in the RA/PC group. RR for RA/PC was 55.8% (95% CI, 46.6% to 64.9%) and for P/PC, 25.4% (95% CI, 21.3 to 29.5%; P = .001). The RA/PC group had a longer median PFS (8.9 v 6.0 months; P = .008). Multivariate analysis of PFS showed significant differences for the RA/PC group (hazard ratio, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.4 to 0.95). No significant differences in toxicity grade 3/4 were found between groups, except for hypertriglyceridemia (10% v 0%) in RA/PC (P = .05). Immunohistochemistry and reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction assays showed expression of RAR-β2 in normal tissues of all tumor samples, but only 10% of samples in the tumor tissue.
Conclusion Adding ATRA to chemotherapy could increase RR and PFS in patients with advanced NSCLC with an acceptable toxicity profile. A phase III clinical trial is warranted to confirm these findings.
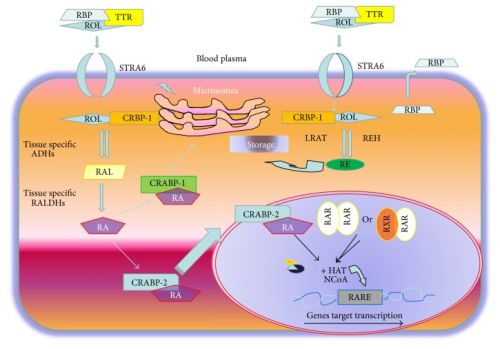
Vitamin A, Cancer Treatment and Prevention: The New Role of Cellular Retinol Binding Proteins
Vitamin A, Cancer Treatment and Prevention: The New Role of Cellular Retinol Binding Proteins
Abstract
Retinol and vitamin A derivatives influence cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis and play an important physiologic role in a wide range of biological processes. Retinol is obtained from foods of animal origin. Retinol derivatives are fundamental for vision, while retinoic acid is essential for skin and bone growth. Intracellular retinoid bioavailability is regulated by the presence of specific cytoplasmic retinol and retinoic acid binding proteins (CRBPs and CRABPs). CRBP-1, the most diffuse CRBP isoform, is a small 15 KDa cytosolic protein widely expressed and evolutionarily conserved in many tissues. CRBP-1 acts as chaperone and regulates the uptake, subsequent esterification, and bioavailability of retinol. CRBP-1 plays a major role in wound healing and arterial tissue remodelling processes. In the last years, the role of CRBP-1-related retinoid signalling during cancer progression became object of several studies. CRBP-1 downregulation associates with a more malignant phenotype in breast, ovarian, and nasopharyngeal cancers. Reexpression of CRBP-1 increased retinol sensitivity and reduced viability of ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Further studies are needed to explore new therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring CRBP-1-mediated intracellular retinol trafficking and the meaning of CRBP-1 expression in cancer patients' screening for a more personalized and efficacy retinoid therapy.
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Longkanker: Immuuntherapie met Nivolumab + chemotherapie geeft op 3-jaars meting bij patienten met operabele niet-kleincellige longkanker (NSCLC) betere ziektevrije overleving (57 procent vs 43 procent) in vergelijking met alleen chemotherapie copy 1
- All-Trans-Retinoic Acid - (Atra is een vorm van vitamine A) gegeven naast chemo bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker zorgt voor significant langere levensduur. aldus gerandomiseerde fase II studie. copy 1
- Selumetinib toegevoegd aan docetaxel geeft aanzienlijk langere progressievrije overleving en langere overall overleving voor patiënten met stadium IIIb en IV niet-klein-cellige longkanker met KRAS mutatie
- Palliatieve behandeling met chemo - gemcitabine of erlotinib - tarceva na eerdere chemo - carboplatin - geeft verbeterde progressie vrije tijd en klein beetje langer leven bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker t.o.v. observatie maar is niet significant
- Chemo combinatie van prednison, azathioprine, en N-acetylcysteine (NAC) voor longfibrose faalt en fase III studie is onmiddelijk stopgezet wegens grote verschil in overlijdenskans in vergelijking met placebogroep
- Chemo: Twee soorten chemo geeft ook bij ouderen verdubbeling van ziektevrije tijd en significant betere overall overleving bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker vergeleken met slechts een vorm van chemo. Blijkt uit fase III studie
- Chemo: Uracil-tagafur (UFT) vergroot kans op vijfjaarsoverleving van 74 procent naar 85 procent bij niet-kleincellige longkankerpatiënten na operatie. Meta analyse bevestigt deze resultaten
- Chemo: Platina gebaseerde chemokuren geven zelfde resultaat op overlevingskansen en overlevingstijd dan niet op platina gebaseerde chemokuren. Echter de bijwerkingen zijn twee tot drie keer zo groot, aldus meta analyse van vele gerandomiseerde studies.
- Gemcitabine als aanvulling op cisplatine gebaseerde chemo en placicataxel bij kleincellige longkanker faalt en leidt tot meer en snellere sterfte blijkt uit grote gerandomiseerde fase III studie (480 deelnemende patiënten)
- Verbeterde vorm van taxol, ook al in Nederland experimenteel toegediend bij patiënten met longkanker. wordt stopgezet na falende veiligheidstesten
- Gemcitabine plus carboplatin is beter te verdragen en geeft beter resultaat dan mitomycin, ifosfamide, en cisplatin (MIC) bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker.
- Chemo toegepast bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker om de tijd te overbruggen in afwachting van bestraling verdubbelt de groei van de tumoren in plaats van verminderen.
- Celebrex - een ontstekingsremmer - zorgt voor goed effect als aanvulling bij chemo bij longkankerpatiënten bewijzen enkele studies
- Platina gebaseerde chemokuren geven zelfde resultaat op overlevingskansen en totale overlevingstijd dan niet platinum gebaseerde chemokuren. Echter de bijwerkingen voor platina gebaseerde chemokuren zijn twee tot drie keer zo veel en ernstiger
- Cisplatin en irinotecan combinatie geeft 19,8% procent kans op tweejaarsoverleving bij kleincellige longkanker
- Tarceva en Iressa werken even effectief als chemo (mediane overleving blijkt hetzelfde) maar met veel minder bijwerkingen bij longkanker
- Genentest voorspelt significant beter of chemo aan zal slaan bij longkankerpatienten of niet.
- Chemo na operatie bij niet-klein-cellige longkankerpatiënten stadium I, II en IIIA heeft geen enkel aantoonbaar positief effect op recidief kansen of succesvolle behandeling
- Chemo bij longkanker: een overzicht van recente ontwikkelingen en belangrijke studie abstracten en artikelen.
- AS1404 - 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid geeft betere resultaten naast chemo bij longkanker dan bij chemo alleen
- Chemo plus bestraling bij oudere mensen met longkanker geeft in vergelijking met alleen bestraling langere levensduur (van 10,5 naar 13,7 maanden mediaan), echter de kwaliteit van leven wordt heel veel slechter
- Chemo: combinatie chemo met Navelbine,- cisplatin en vinorelbine geeft bij longkankerpatiënten (stadium I en II) positief effect op vijf jaars overleving blijkt uit 10 jarige gerandomiseerde placebo gecontroleerde fase III studie bij 482 patiënten.
- Chemo: Irinotecan plus Gemcitabine geeft tegenover alleen irinotecan geen verschil bij gevorderde niet-kleincellige longkanker in overleving en tijd tot recidief, wel iets minder bijwerkingen,maar ook deze waren niet significant
- Chemo: Thalidomide naast chemo geeft kortere mediane overleving voor niet-klein-cellige longkanker en ernstiger bijwerkingen (trombose) in vergelijking met placebo. Aldus gerandomiseerde placebo gecontroleerde fase III studie.
- Chemo bij longkanker: overzicht van recente ontwikkelingen en belangrijke studies



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "All-Trans-Retinoic Acid - (Atra is een vorm van vitamine A) gegeven naast chemo bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker zorgt voor significant langere levensduur. aldus gerandomiseerde fase II studie. copy 1"