11 augustus 2018: Zie ook dit artikel:
11 april 2014: Bron: Arch Med Sci. 2014 Feb 24;10(1):1-9. Epub 2014 Feb 23
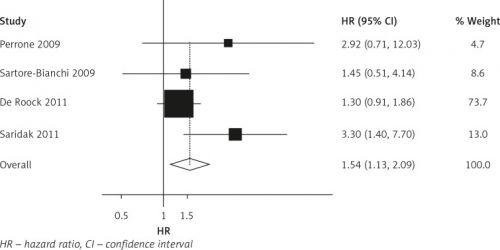
PIK3CA mutaties in z'n geheel, maar vooral een afwijking in PIK3CA exon 20 kan voorspellen dat een anti-EGFR MoAb gebaseerde chemotherapie bij patiënten met uitgezaaide darmkanker met het KRAS wild type weinig tot geen effectieve behandeling zal zijn. Opnieuw een reden te meer om het pathologisch rapport uit te breiden tot een volledig biomoleculair onderzoek, zodat een patiënt ook echt een behandeling binnen personalised medicine krijgt.
Conclusie uit de studie: Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody-based therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of the effect of PIK3CA mutations in KRAS wild-type patients. waarvan het volledige studierapport gratis is in te zien luidt:
CONCLUSIONS:
PIK3CA mutations as a whole might be useful prognostic factors for assessing clinical outcomes of anti-EGFR MoAb-based chemotherapies in KRAS wild-type mCRC patients. In particular, PIK3CA exon 20 mutations were significantly associated with lack of response.
Hier het abstract plus referentielijst van de studie: Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody-based therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of the effect of PIK3CA mutations in KRAS wild-type patients
Overall, our meta-analysis showed that PIK3CA mutations as a whole might be useful prognostic factors for assessing clinical outcomes and further confirmed that PIK3CA mutation on exon 20 decreases the response rate of anti-EGFR MoAb-based chemotherapies in wild-type KRAS mCRC patients. But we could not exclude the potential confounding by the interaction effect of other mutations which frequently associated with PIK3CA exon 20 mutations. We also strongly recommend that exon 9 and 20 mutations be studied separately.
Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody-based therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of the effect of PIK3CA mutations in KRAS wild-type patients
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Moleculaire schakelaar verandert kankercellen in weer normale cellen en zou genezende aanpak van kanker kunnen betekenen copy 1
- Bispecifieke anti-lichaam REGN7075 in combinatie met Libtayo (cemiplimab) geeft veelbelovende resultaten bij patiënten met microsatelliet-stabiele darmkanker die ongevoelig zijn voor immuuntherapie
- 10-genentest voorspelt welke chemo het beste zou zijn voor patienten met darmkanker stadium II en III na operatie.
- Biomarkers zijn waardevol voor een gepersonaliseerde behandeling van darmkanker, bewijst de TAPUR-studie
- Overzicht van studies met medicijnen en behandelingen om tumoren met KRAS mutaties aan te pakken. Vooral combinatiebehandelingen zijn veelbelovend. copy 1 copy 1
- Temozolomide - temodal gevolgd door immunotherapie met combinatie van lage dosis ipilimumab plus nivolumab geeft hoopgevende resultaten bij patiënten met microsatellietstabiel en MGMT-gedempte uitgezaaide darmkanker copy 1
- NUC-3373, een thymidylate synthase remmer, geeft opmerkelijk goede resultaten zonder de bekende bijwerkingen bij zwaar voorbehandelde patiënten met uitgezaaide darmkanker
- Darmkankerpatienten stadium III met een instabiele MSI/dMMR leefden langer met een recidief dan met MSI/dMMR stabiel voordat immuuntherapie kon worden ingezet
- POLE mutatie: veel kankerpatienten met erfelijke vormen van kanker hebben naast een P1-ligand een POLE mutatie en reageren goed op immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen - checkpointremmers als pembrolizumab en nivolumab copy 1
- Anti-EGFR anti body mix van medicijnen - SYM004 - geeft hoopvolle resultaten in fase I studie bij zwaar voorbehandelde darmkankerpatienten met RAS en EGFR positieve mutaties
- BRAF en EGFR mutaties gerichte medicijnencocktail zou ontduiking tegen het nieuwe succesvolle eiwit molecuul - PLX4032 - vemurafenib bij darmkanker opheffen, aldus Nederlandse onderzoekers
- Cimetidine - Tagamet-800 - een maagzuurremmer bewijst bij maagkanker en darmkanker een effectieve kankerremmer te zijn.
- Debulking plus op receptoren - mutaties gerichte aanpak voor in lever of andere organen uitgezaaide darmkanker wordt in fase I onderzocht in Nederland.
- DNA mutaties komen 3x zo vaak voor bij jonge mensen (gemiddeld 40 jaar) dan bij ouderen (gemiddeld 70 jaar) met darmkanker. copy 1
- Erbitux - Cetuximab faalt als aanvulling bij chemo (FOLFOX) voor darmkankerpatienten. Fase III studie is daarom afgebroken. Bij KRAS wild type werkt Erbitux wel.
- Klinische en genetische factoren voorspellen een eventuele respons op een behandeling bij patiënten met de ziekte van Crohn
- KRAS en NRAS mutatie bepaling cruciaal voor effectieve anti-EGFR behandeling bij uitgezaaide darmkanker met FOLFOX4 + Panitumumab
- Mifeprestone - (RU-486) - abortuspil stopt tumorgroei bij darmkankerpatienten met veruitgezaaide darmkanker en stopt ook groei van kanker bij andere vormen van kanker blijkt uit studies.
- Mutaties in andere genen - Nras, BRAF, PIK3CA en niet-functionele PTEN voorspellen uitkomsten en resistentie van anti-EGFR behandelingen bij KRAS wild type en toont de noodzaak van uitgebreidere biomarker analyse bij uitgezaaide darmkanker copy 1
- Nivolumab goedgekeurd door FDA voor MSI-H of dMMR uitgezaaide darmkanker na progressie van de ziekte gedurende of na chemo met FOLFOX en Folfirinox
- Onvansertib naast standaard chemotherapie krijgt van FDA versnelde goedkeuring na uitstekende resultaten bij darmkanker KRAS positief
- PIK3CA mutaties en vooral in PIK3CA exon 20 voorspellen gebrek aan respons voor anti-EGFR medicijnen bij uitgezaaide darmkanker met KRAS wild type
- Plaats van de tumor - rechts of links - heeft grote invloed op overall overleving en op keuze voor cetuximab of bevacizumab - avastin als behandeling voor uitgezaaide darmkanker KRAS wild type
- Panitumubab en Avastin bij darmkanker, een paar studies en een artikel in Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde over targeted therapie bij darmkankers.
- Raltritexed: Analyse van effect en kosten van irinotecan, oxaliplatin en raltitrexed al of niet in combinaties ten opzichte van 5-FU bij darmkanker.
- Regorafenib krijgt goedkeuring van de Europese Commissie voor het gebruik bij uitgezaaide darmkanker waarbij eerdere behandelingen falen.
- Uracil-tegafur (UFT) geeft zelfde resultaat bij uitgezaaide darmkanker als intraveneuze chemo (5-FU en leucovorin) maar veel minder bijwerkingen en veel gemakkelijker in te nemen
- Spectacolor studie bij darmkanker toont aan dat receptoren- en DNA onderzoek cruciaal is voor nieuwe op te zetten klinische studies en een goede optimale gepersonaliseerde behandeling bij darmkanker copy 1
- Sotorasib (AMG 510) geeft bij patienten met KRAS G12C mutatie bij patienten met zwaar voorbehandelde darmkanker en longkanker met KRAS pos. alsnog uitstekende resultaten copy 1 copy 1
- Vedolizumab voorkomt en geneest ontstekingen in darmen en lijkt uitstekend medicijn bij ziekte van Crohn
- Vinorelbine lijkt voor darmkanker met BRAF en KRAS mutatie een effectief medicijn aldus Rene Bernards na nieuwe studieresultaten uit basket studies
- Xilonix - MAPp1 zorgt voor stabiele ziekte (bij 53 procent) bij zwaar voorbehandelde darmkankerpatienten stadium 4 met een mediane overall overleving van 4.2 maanden vs 11.5 maanden in vergelijking met placebo
- Personalised medicin en gerichte aanpak - targeted therapy - op veel voorkomende receptoren en genmutaties bij vormen van darmkanker bij elkaar gezet in een overzicht



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "PIK3CA mutaties en vooral in PIK3CA exon 20 voorspellen gebrek aan respons voor anti-EGFR medicijnen bij uitgezaaide darmkanker met KRAS wild type"