Helpt u ons aan 500 donateurs?
15 augustus 2025: lees ook dit artikel: https://kanker-actueel.nl/lorlatinib-geeft-veel-langere-progressievrije-ziekte-dan-crizotinib-bij-patienten-met-gevorderde-uitgezaaide-niet-kleincellige-longkanker-met-alk-mutatie.html
19 april 2018: Bron: Journal of Clinical Oncology
Ook bij zwaar voorbehandelde longkankerpatiënten met niet-kleincellige longkanker de zogeheten ROS1 mutatie (c-ros oncogene 1) (1 tot 2 procent van de longkankerpatiënten heeft deze mutatie) blijkt crizotinib alsnog bijzonder effectief. Uit een fase I/II studie blijkt van de 127 deelnemende patiënten 71.7% (95% CI, 63.0% to 79.3%), goed te reageren op crizotinib met maar liefst 17 complete remissies (CR) en 74 gedeelteljike remissies (PR = 50 procent of meer vermindering van tumoromvang en tumor aantal).
Het volledige studierapport: Phase II Study of Crizotinib in East Asian Patients With ROS1-Positive Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer is tegen betaling in te zien. Het abstract hiervan staat onderaan artikel en lees ook onderstaand artikel uiteraard.
10 april 2017: lees ook dit artikel:
12 maart 2016: De FDA - Food and Drug Adminstration geeft ook toestemming voor gebruik van crizotinib (Xalkori) voor longkanker met de zogeheten ROS-1 mutatie. Nadat een studie met 50 longkankerpatiënten heeft laten zien dat crizotinib bij deze mutatie voor nagenoeg dezelfde resultaten zorgt en met een zelfde bijwerkingenprofiel als bij longkanker met een ALK mutatie.
De studie evalueerde 50 patiënten (leeftijd 25 tot 77 jaar) van wie de tumoren een ROS1-positieve mutatie vertoonde geconstateerd door een receptoranalyse via 'fluorescence in situ hybridization' (96%) of door een 'reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction' (4%).
De objectieve response vastgesteld door een scan was 66% (95% confidence interval = 51%–79%) met een duur van de respone van mediaan 18 maanden. De objectieve response was 72% (95% CI = 58%–84%).
Klik hier voor het persbericht van de FDA.
22 december 2014: aan onderstaand artikel kan ik deze publicatie in NEJM d.d. december 2014 toevoegen:
Crizotinib was superior to standard first-line pemetrexed-plus-platinum chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated advanced ALK-positive NSCLC. (Funded by Pfizer; PROFILE 1014 ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01154140.)
9 juli 2014: ik heb aan onderstaande informatie het abstract van het volledige studierapport: Development of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors and molecular diagnosis in ALK rearrangement-positive lung cancer dat gratis is in te zien toegevoegd. Dit volledige studierapport geeft mooi overzicht van de aanpak van vormen van longkanker met ALK mutatie. Zie onderaan abstract met interessante referentielijst.
15 mei 2014: Lees ook artikel aanvullend op onderstaand artikel:
Afgelopen week bezocht ik een lezing van prof. dr. Bernards bij de KNAW over een kanker behandeling op maat en hij gebruikte crizotinib als voorbeeld van een succesvol medicijn dat op basis van een receptoren- en DNA onderzoek bij longkanker met ALK mutatie is ontwikkeld en voor hele goede resultaten zorgt bij longkankerpatiënten met de juiste mutatie. En vertelde ook hoe belangrijk het is om de EGFR mutatie te meten en de daaronder liggende andere mutaties en receptorenexpressie.
1 oktober 2012: Bron: ESMO 2012
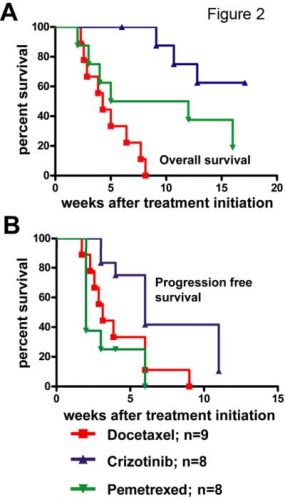
Crizotinib is superieur aan pemetrexed - Alimta of chemo - docetaxel bij gevorderde niet-klein-cellige longkanker stadium IIIB/IV met ALK positieve mutatie. Dit tonen de resultaten aan van een Fase III studie en werd gepresenteerd op ESMO 2012 in Wenen. Longartsen stellen dat crizotinib nu eerste lijns behandeling moet worden voor niet-klein-cellige longkanker met ALK positieve mutatie.
In deze studie met totaal 347 patiënten met niet-klein-cellige longkanker die allemaal eerder met chemo waren behandeld werd crizotinib vergeleken met op platina gebaseerde chemo plus pemetrexed - Alimta. Uit de studie kwam naar voren dat met name voor patiënten waarbij de ALK mutatie positief was getest crizotinib een hoog significante verbetering te zien gaf van de progressie vrije tijd en overall overlevingstijd en kwaliteit van leven. Volgens de onderzoekers voldoet slechts 5% van de mensen met niet-klein-cellige longkanker aan een ALK positieve mutatie. Wat natuurlijk niet wegneemt dat als u tot die groep behoort er een nieuwe mogelijkheid is.tot behandeling. Klik hier voor meer informatie over crizotinib, zoals bijwerkingen enz.
De gerandomiseerde fase III studie vergeleek de werkzaamheid en veiligheid van crizotinib met standaard chemotherapie met pemetrexed - Alimta of docetaxel, in 347 patiënten met ALK-positieve, stadium IIIB / IV niet-klein-cellige longkanker (NSCLC) die reeds eerder waren behandeld met chemotherapie.
De groep die crizotinib kreeg had een significant langere progressievrije overleving met mediaan 7,7 maanden in vergelijking tot 3,0 maanden bij patiënten die alleen chemo hadden ontvangen
(HR 0,49, 95% CI 0,37-0.64, p <0,0001). Het totale respons percentage was ook significant hoger bij patiënten behandeld met crizotinib (65% vs 20%, p <0,0001).
Over de totale overleving is nog geen onderbouwde conclusie te trekken omdat de studie nog loopt en het eind van de studie nog niet is bereikt. Maar er is op dit moment al een significante cross-over in de studie gezien waarin de patiënten die als eerste werden ingedeeld in de chemogroep en ziekte progressie lieten zien en daarna naar de crizotinib groep mochten overstappen. Vandaar dat ook een meerderheid van de patiënten uit de chemogroep ook in feite crizotinib hebben gekregen en dit maakt de bepaling van de totale overleving ingewikkeld.
Duur van de behandeling was langer voor crizotinib waarmee gemiddeld 11 cycli werden gegeven in vergelijking met 4 cycli met pemetrexed - Alimta of docetaxel. Ook dit geeft aan dat crizotinib veruit superieur was aan chemo plus Alimta of chemo alleen.
De meest voorkomende behandeling gerelateerde bijwerkingen met crizotinib werden gemeld door 59% van de patiënten, 53% meldden diarree, 52% misselijkheid, braken 44% en 36% van de
patiënten verhoogde transaminasen (giststof). Bijwerkingen, waaronder misselijkheid, vermoeidheid, neutropenie, verminderde eetlust, en haaruitval werden gemeld door 35%, 29% 22% 21% en 20%
van de patiënten die pemetrexed - Alimta of docetaxel hadden ontvangen. Alle behandelgroepen hadden dezelfde incidentie van graad 3/4 behandeling gerelateerde bijwerkingen van 31%. Zes procent van crizotinib patiënten in vergelijking met 10% van pemetrexed / docetaxel patiënten stopten met het onderzoek vanwege de behandeling gerelateerde bijwerkingen. Echter, ondanks de bijwerkingen, rapporteerden de patiënten nog steeds verbeterde kwaliteit van leven met crizotinib in vergelijking met chemo.
Conclusie gebaseerd op dit onderzoek is dat na de wereldwijde implementatie van gerichte therapie bij longkanker patiënten gedefinieerd door EGFR-mutatie (Tarceva - Iressa zijn de meest gebruikte medicijnen darvoor), dit de tweede groep is van patiënten met niet-kleincellige longkanker die duidelijk baat hebben bij een behandeling die direct gericht is op een moleculaire verandering. De resultaten van dit onderzoek is een belangrijke stap naar meer geïndividualiseerde therapie bij longkankerpatiënten, aldus aanwezige longspecialiste in Wenen.
Hier het abstract van deze studie zoals gepresenteerd in Wenen en waaruit bovenstaand artikel is samengesteld.
Phase III trial shows crizotinib superior to single-agent chemotherapy for ALK-positive advanced NSCLC
30.09.12
Category: Vienna 2012 Congress, Vienna 2012 App
Crizotinib superior to pemetrexed or docetaxel in the first head-to-head comparison study
The results of a new phase III trial show that crizotinib is more effective treatment than standard chemotherapy for patients with advanced, ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), who have been previously treated with first-line, platinum-based chemotherapy. The study results are reported at the ESMO 2012 Congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology in Vienna.
Rearrangements of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene are found in about 5% of all NSCLC. In previous studies, crizotinib has been shown to induce significant clinical responses in patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC, but this is the first phase III study in this setting.
This study is also the first head-to-head comparison of crizotinib with standard chemotherapy and according to the lead study author, Dr Alice Shaw from Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center, Boston, USA, crizotinib is superior to standard single-agent chemotherapy in terms of response, progression-free survival and quality of life in ALK-positive patients who have been previously treated with first-line, platinum-based chemotherapy. These results establish crizotinib as the standard of care for patients with advanced, previously treated, ALK-positive NSCLC.
The current global randomized phase III study compared the efficacy and safety of crizotinib with standard chemotherapy with pemetrexed or docetaxel, in 347 patients with ALK-positive, stage IIIB/IV NSCLC who had already been treated with chemotherapy.
The study showed that crizotinib prolonged progression-free survival to a median of 7.7 months compared to 3.0 months among those patients who received the chemotherapy (HR 0.49; 95% CI 0.37–0.64; p < 0.0001). The overall response rate was also significantly higher in those treated with crizotinib (65% vs 20%; p < 0.0001). So far, the analysis of the overall survival rate with the two drugs is still immature, and there are no enough events to draw meaningful conclusions.
There was significant crossover in the study, patients who were randomized to receive chemotherapy and had disease progression were allowed to crossover to receive crizotinib. Hence, the majority of patients on the chemotherapy arm actually did receive crizotinib and this makes determination of overall survival benefit very challenging. Duration of treatment was longer for crizotinib where a median of 11 cycles compared to 4 with pemetrexed or docetaxel were started by patients.
The most common treatment-related adverse events with crizotinib were reported by 59% of patients, 53% diarrhea, 52% had nausea, 44% vomiting and 36% of patients reported elevated transaminases. Adverse events including nausea, fatigue, neutropenia, decreased appetite, and alopecia were reported by 35%, 29% 22% 21% and 20% of patients receiving pemetrexed or docetaxel. All treatment groups had the same incidence of grade 3/4 treatment related adverse events of 31%. Six percent of crizotinib patients compared to 10% of pemetrexed/docetaxel patients discontinued the trial due to treatment related adverse events. However, despite side effects, patients still reported improved quality of life on crizotinib compared with chemotherapy.
Commenting on clinical relevance of these data, Dr Enriqueta Felip, Head of the Lung Cancer Unit in Oncology Department at Vall d'Hebron University Hospital in Barcelona, Spain, and chair of the ESMO 2012 Metastatic NSCLC program track (who was not involved in the study) said that crizotinib, an oral drug, is more effective than standard chemotherapy in previously treated patients with advanced NSCLC with a specific molecular alteration, ALK. This is the first randomized study in this group of patients selected precisely because they have ALK-positive tumors.
After the worldwide implementation of targeted therapy in lung cancer patients defined by EGFR mutation, this is the second group of patients with non-small cell lung cancer to clearly benefit from a therapy directly targeting a molecular alteration. The results of this study represent a significant step towards more individualized therapy in lung cancer patients.
The improvement and validation of methods for the detection of ALK rearrangement in NSCLC patients will be key to the optimal clinical use of ALK inhibitors.
Development of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors and molecular diagnosis in ALK rearrangement-positive lung cancer
Abstract
The fusion of echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) was identified as a transforming gene for lung cancer in 2007. This genetic rearrangement accounts for 2%–5% of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cases, occurring predominantly in younger individuals with adenocarcinoma who are never- or light smokers. A small-molecule tyrosine-kinase inhibitor of ALK, crizotinib, was rapidly approved by the US Food and Drug Administration on the basis of its pronounced clinical activity in patients with ALK rearrangement-positive NSCLC. Next-generation ALK inhibitors, such as alectinib, LDK378, and AP26113, are also being developed in ongoing clinical trials. In addition, the improvement and validation of methods for the detection of ALK rearrangement in NSCLC patients will be key to the optimal clinical use of ALK inhibitors. We here summarize recent progress in the development of new ALK inhibitors and in the molecular diagnosis of ALK rearrangement-positive NSCLC.
References
This study demonstrated clinically meaningful benefit and durable responses with crizotinib in East Asian patients with ROS1-positive advanced NSCLC. Crizotinib was generally well tolerated, with a safety profile consistent with previous reports.
ORIGINAL REPORTS
Thoracic Oncology
Phase II Study of Crizotinib in East Asian Patients With ROS1-Positive Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Approximately 1% to 2% of non–small-cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) harbor a c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) rearrangement. Crizotinib, an inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), ROS1, and MET, has shown marked antitumor activity in a small expansion cohort of patients with ROS1-positive advanced NSCLC from an ongoing phase I study. We assessed the efficacy and safety of crizotinib in the largest cohort of patients with ROS1-positive advanced NSCLC.
This phase II, open-label, single-arm trial enrolled East Asian patients with ROS1-positive (assessed through validated AmoyDx assay [Amoy Diagnostics, Xiamen, China] at three regional laboratories) advanced NSCLC who had received three or fewer lines of prior systemic therapies. Patients were to receive oral crizotinib at a starting dose of 250 mg twice daily and continued treatment until Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1–defined progression (by independent radiology review ), unacceptable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent. The primary end point was objective response rate (ORR) by IRR.
In the efficacy and safety analyses, 127 patients were included, with 49.6% still receiving treatment at data cutoff. ORR by IRR was 71.7% (95% CI, 63.0% to 79.3%), with 17 complete responses and 74 partial responses. ORRs were similar irrespective of the number of prior lines of therapy, and responses were durable (median duration of response, 19.7 months; 95% CI, 14.1 months to not reached). Median progression-free survival by IRR was 15.9 months (95% CI, 12.9 to 24.0 months). No new safety signals associated with crizotinib were reported.
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Crizotinib en alectinib, twee ALK-remmers, blijken uitstekende resultaten te geven voor niet-klein-cellige longkanker met ALK pos. mutaties, zelfs voor patienten met hersenuitzaaiingen
- Tyrosine Kinase remmers (TKI) bij longkanker met EGFR mutaties. Een overzicht van artikelen van verschillende TKI remmers.



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Crizotinib is superieur aan pemetrexed - Alimta of chemo - docetaxel bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker met ALK positieve genmutatie"