28 november 2019: Lees ook dit artikel:
10 februari 2015: Bron: the Lancet
Avastin - bevacizumab geeft geen verbetering in kwaliteit van leven en pijn, in tegendeel patiënten die enkele maanden langer leefden ervaarden meer pijn en slechtere kwaliteit van leven. Aldus blijkt uit de definitieve studiersultaten van onderstaand beschreven studie. Toevoeging van Avastin- bavacizumb aan cisplatin of topotecan ljkt dan ook weinig zin te hebben, aldus de onderzoekers. Wederom wordt Avastin - bavacizumab dus afgeserveerd in de eindconclusie van een grote fase III studie.
Voor het volledige studierapport dat aantoonde dat Avastin - bevacizumab enkele maanden (3,7 maanden mediaan) langere levensduur liet zien en dat gratis is in te zien, klikt u op de volgende link: Improved Survival with Bevacizumab in Advanced Cervical Cancer
Voor het volledige studierapport over kwaliteit van leven uit dezelfde studie, waarvoor u moet betalen vreemd genoeg, klikt u op de volgende link: Bevacizumab for advanced cervical cancer: patient-reported outcomes of a randomised, phase 3 trial (NRG Oncology–Gynecologic Oncology Group protocol 240)
Abstracten staan onderaan artikel en lees ook onder grafiekbeeld over deze studies.
10 februari 2013: bron: National Cancer Institute (NCI).
Bevacizumab - Avastin geeft significant langere overleving bij patiënten met gevorderde baarmoederhalskanker of een recidief van baarmoederhalskanker waar een andere aanpak, zoals chirurgie en / of bestraling niet leidde tot genezing, blijkt uit een tussenevaluatie van een grote gerandomiseerde fase III studie van het National Cancer Institute (NCI).
Deze grote gerandomiseerde klinische studie staat bekend als GOG 240 (Gynaecologische Oncology Group 240. Volgens de auteurs zullen de gegevens uit deze studie de tweede lijns aanpak van baarmoederhalskanker waarschijnlijk veranderen. Nu hebben we dit al vaker gehoord bij tussenevaluties van Avastin - Bavacizumab bij o.a. darmkanker en borstkanker maar afgaande op de resultaten die nu gemeld worden zou Avastin - bevacizumab wel een rol kunnen gaan spelen in de aanpak van baarmoederhalskanker.
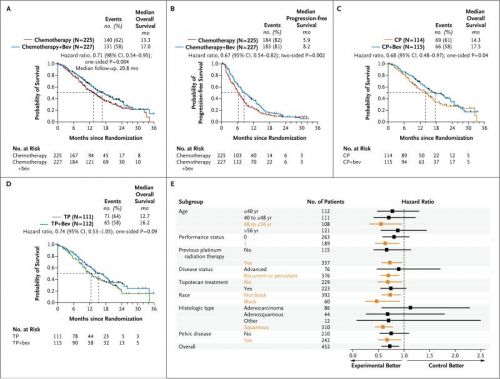
De mediane overleving was 3,7 maanden langer bij vrouwen behandeld met chemotherapie plus avastin - bevacizumab dan bij degenen die behandeld werden met alleen chemotherapie (17,0 vs 13,3 maanden). Dit blijkt een statistisch significant verschil te zijn, aldus de onderzoekers. Wat deze resultaten ook geloofwaardig maakt is dat het onafhankelijke NCI deze studie uitvoert en niet de producent zelf. Aan de andere kant is een studietijd van drie jaar wel tamelijk kort om de mediane overleving vast te stellen. Maar er zijn wel veel deelnemende patiënten (n = 452) en dat maakt het toch weer geloofwaardiger
Aan de studie doen totaal 452 patiënten met voorbehandelde uitgezaaide of teruggekeerde (recidief) of gevorderde baarmoederhalskanker mee. Het onderzoek werd uitgevoerd in verschillende ziekenhuizen in Spanje en Amerika. De patiënten stroomden in de studie in de periode 2009-2012.
In deze studie onderzoeken de onderzoekers of topotecan of cisplatin beter zou zijn in combinatie met paclitaxel en of de toevoeging van avastin - bevacizumab de mediane overleving verbetert in beide schema's. Er zijn dus vier behandelgroepen. Cisplatin plus paclitaxel en met of zonder avastin - bevacizumab. En topotecan plus paclitaxel en wel of geen avastin - bevacizumab. De patiënten werden willekeurig (gerandomiseerd) ingedeeld in een van de 4 groepen.
In een tussentijdse analyse in 2012 (let wel dit is voor een aantal patiënten pas het eerste jaar na start van de behandeling en kan nog van invloed zijn op de mediane overleving de komende jaren) werd er tussen topotecan plus paclitaxel in vergelijking met cisplatin plus paclitaxel geen significant verschil gevonden in mediane overleving en ziektevrije tijd. Voor de toevoeging van avastin - bevacizumab werd echter door de twee groepen heen wel een significant verschil gevonden van 3,7 maanden in mediane overlevingstijd.
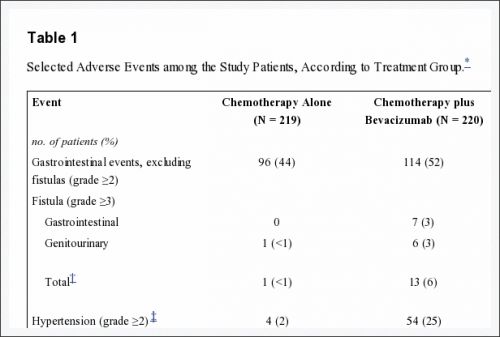
In deze studie werd avastin - bevacizumab intraveneus toegediend in een dosis van 15 mg / kg lichaamsgewicht, in combinatie met chemotherapie en werd toegediend 1 dag per elke 3 weken tot zich ziekteprogressie of onaanvaardbare toxiciteit (bijerkingen) optrad. De combinatie behandeling met Avastin - bevacizumab resulteerde wel in meer bijwerkingen dan bij chemotherapie alleen. De onderzoekers van het NCI merken wel op dat de nadelige effecten conform en consistent waren met eerder bekende bijwerkingen geassocieerd met avastin - bevacizumab.
Op ASCO 2013 in juni zullen de volledige gegevens worden gepubliceerd. Op dit moment is er nog geen abstract of studierapport gepubliceerd. Medscape meldde dit nieuws en bovenstaand artikel heb ik uit hun artikel gecomponeerd en vrij vertaald.
Voor het volledige studierapport dat aantoonde dat Avastin - bevacizumab enkele maanden (3,7 maanden mediaan) langere levensduur liet zien en dat gratis is in te zien, klikt u op de volgende link: Improved Survival with Bevacizumab in Advanced Cervical Cancer
Voor het volledige studierapport over kwaliteit van leven uit dezelfde studie, waarvoor u moet betalen vreemd genoeg, klikt u op de volgende link: Bevacizumab for advanced cervical cancer: patient-reported outcomes of a randomised, phase 3 trial (NRG Oncology–Gynecologic Oncology Group protocol 240)
Hieronder respectievelijk de abstracten van de studies:
Improvements in overall survival and progression-free survival attributed to the incorporation of bevacizumab into the treatment of advanced cervical cancer were not accompanied by any significant deterioration in health-related quality of life.
Source: The Lancet: DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70004-5
Bevacizumab for advanced cervical cancer: patient-reported outcomes of a randomised, phase 3 trial (NRG Oncology–Gynecologic Oncology Group protocol 240)
Summary
Background
GOG 240 was a practice-changing randomised phase 3 trial that concluded that chemotherapy plus bevacizumab for advanced cervical cancer significantly improves overall and progression-free survival, and the proportion of patients achieving an overall objective response, compared with chemotherapy alone. In this study, we aimed to analyse patient-reported outcomes in GOG 240.
Methods
Eligible adult participants (aged ≥18 years) had primary stage IVB or recurrent or persistent carcinoma of the cervix with measurable disease and GOG performance status of 0–1. Participants were randomly assigned by web-based permuted block randomisation (block size 4) in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to the four treatment groups: cisplatin (50 mg/m2 intravenously on day 1 or 2 of the treatment cycle) and paclitaxel (135 mg/m2 intravenously over 24 h or 175 mg/m2 intravenously over 3 h on day 1), with or without bevacizumab (15 mg/kg intravenously on day 1 or 2), or paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 over 3 h on day 1) and topotecan (0·75 mg/m2 for 30 min on days 1–3) with or without bevacizumab (15 mg/kg intravenously on day 1). Treatment assignment was concealed at randomisation (everyone was masked to treatment assignment, achieved by the use of a computer encrypted numbering system at the National Cancer Institute) and became open-label when each patient was registered to the trial. Treatment cycles were repeated every 21 days until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, whichever occurred first. The coprimary endpoints of the trial were overall survival and safety; the primary quality-of-life endpoint was the score on the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Cervix Trial Outcome Index (FACT-Cx TOI). For our analysis of patient-reported outcomes, participants were assessed before treatment cycles 1, 2, and 5, and at 6 and 9 months after the start of cycle 1, with the FACT-Cx TOI, items from the FACT-GOG-Neurotoxicity subscale, and a worst pain item from the Brief Pain Inventory. All patients who completed baseline quality-of-life assessments and at least one further follow-up assessment were evaluable for quality-of-life outcomes. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT00803062.
Findings
Between April 6, 2009, and Jan 3, 2012, a total of 452 patients were enrolled in the trial, of whom 390 completed baseline quality-of-life assessment and at least one further assessment and were therefore evaluable for quality-of-life outcomes. In these patients, patient-reported outcome completion declined from 426 (94%) of 452 (at baseline) to 193 (63%) of 307 (9 months post-cycle 1), but completion rates did not differ significantly between treatment regimens (p=0·78). The baseline FACT-Cx TOI scores did not differ significantly between patients who received bevacizumab versus those who did not (p=0·27). Compared with patients who received chemotherapy alone, patients who received chemotherapy plus bevacizumab reported FACT-Cx TOI scores that were an average of 1·2 points lower (98·75% CI −4·1 to 1·7; p=0·30).
Interpretation
Improvements in overall survival and progression-free survival attributed to the incorporation of bevacizumab into the treatment of advanced cervical cancer were not accompanied by any significant deterioration in health-related quality of life. Patients responding to anti-angiogenesis therapy who maintain an acceptable quality of life could be suitable at progression for treatment with other novel therapies that might confer additional benefit.
Funding
National Institutes of Health.
Improved survival with bevacizumab in advanced cervical cancer.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) promotes angiogenesis, a mediator of disease progression in cervical cancer. Bevacizumab, a humanized anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody, has single-agent activity in previously treated, recurrent disease. Most patients in whom recurrent cervical cancer develops have previously received cisplatin with radiation therapy, which reduces the effectiveness of cisplatin at the time of recurrence. We evaluated the effectiveness of bevacizumab and nonplatinum combination chemotherapy in patients with recurrent, persistent, or metastatic cervical cancer.
METHODS:
Using a 2-by-2 factorial design, we randomly assigned 452 patients to chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab at a dose of 15 mg per kilogram of body weight. Chemotherapy consisted of cisplatin at a dose of 50 mg per square meter of body-surface area, plus paclitaxel at a dose of 135 or 175 mg per square meter or topotecan at a dose of 0.75 mg per square meter on days 1 to 3, plus paclitaxel at a dose of 175 mg per square meter on day 1. Cycles were repeated every 21 days until disease progression, the development of unacceptable toxic effects, or a complete response was documented. The primary end point was overall survival; a reduction of 30% in the hazard ratio for death was considered clinically important.
RESULTS:
Groups were well balanced with respect to age, histologic findings, performance status, previous use or nonuse of a radiosensitizing platinum agent, and disease status. Topotecan-paclitaxel was not superior to cisplatin-paclitaxel (hazard ratio for death, 1.20). With the data for the two chemotherapy regimens combined, the addition of bevacizumab to chemotherapy was associated with increased overall survival (17.0 months vs. 13.3 months; hazard ratio for death, 0.71; 98% confidence interval, 0.54 to 0.95; P=0.004 in a one-sided test) and higher response rates (48% vs. 36%, P=0.008). Bevacizumab, as compared with chemotherapy alone, was associated with an increased incidence of hypertension of grade 2 or higher (25% vs. 2%), thromboembolic events of grade 3 or higher (8% vs. 1%), and gastrointestinal fistulas of grade 3 or higher (3% vs. 0%).
CONCLUSIONS:
The addition of bevacizumab to combination chemotherapy in patients with recurrent, persistent, or metastatic cervical cancer was associated with an improvement of 3.7 months in median overall survival. (Funded by the National Cancer Institute; GOG 240 ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00803062.).
Comment in
- Targeted therapies: Further delineating bevacizumab's response spectrum. [Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014]
- PMID:
- 24552320
- [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
- PMCID:
- PMC4010094
Gerelateerde artikelen
- chemotherapie vooraf aan standaard behandeling met radiotherapie plus chemotherapie voor lokaal gevorderde baarmoederhalskanker geeft betere resultaten dan alleen standaard behandeling van bestraling plus chemotherapie
- Chemo gevoeligheidstest naar cisplatin vooraf aan behandeling van baarmoederhalskanker met chemo plus bestraling maakt verschil van 25 procent op twee jaars ziektevrije overleving tussen responders en niet responders.
- Avastin - bevacizumab naast chemo verbetert met 3,7 maanden overleving voor gevorderde uitgezaaide of recidief van baarmoederkanker waar andere aanpak van operatie en bestraling faalde. copy 1
- Chemo bij baarmoederhalskanker: pre-operatieve chemo bij baarmoederhalskanker lijkt weinig toe te voegen aan kansen op recidief en overall overlevingskansen blijkt uit meta analyse van Cochrane instituut. Artikel update 27 september 2010




Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Avastin - bevacizumab naast chemo verbetert met 3,7 maanden overleving voor gevorderde uitgezaaide of recidief van baarmoederkanker waar andere aanpak van operatie en bestraling faalde. copy 1"