16 juli 2020: lees ook dit artikel:
14 september 2017:
op ESMO 2017 is onderstaande studie gepresenteerd met deze resultaten. klik op de volgende link voor volledige tekst: CheckMate-214, combined nivolumab and ipilimumab shows considerable benefit in intermediate- and poor-risk patients with advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma
...............
The benefit from the immunotherapy combination in intermediate/high risk patients
After approximately 17.5 months of follow-up, CheckMate-214 met the co-primary endpoint of ORR in intermediate/poor risk patients, which was 41.6% for the nivolumab/ipilimumab combination compared to 26.5% for sunitinib (p < 0.0001) with 9.4% of patients receiving combination therapy achieving complete response (CR) compared to1.2% of patients on sunitinib.
The median duration of response (DoR) was not reached (95% confidence interval 21.82, NR) versus 18.2 months with sunitinib (95% CI 14.82, NR).
There was an improvement in median PFS with the combination in this cohort;median PFS was 11.6 months for the nivolumab and ipilimumab combination versus 8.4 months with sunitinib, hazard ratio 0.82 (p = 0.03).
The efficacy outcomes differed according to the levels of PD-L1 expression and IMDC risk group
Both the ORR per indipendent committee and PFS significantly favoured nivolumab plus ipilimumab over sunitinib in intermediate/poor risk patients having baseline PD-L1 expression ≥1% where the ORR was 58% versus 25%, and median PFS was 22.8 (95% CI 9.4, NR) months versus 5.9 (95% CI 4.4, 7,1) months, respectively, HR 0.48 (95% CI 0.28, 0.82; p = 0.0003).
The investigators found that baseline tumour PD-L1 expression was lower in the cohort of patients at favourable risk where 11% of patients on combination had PD-L1 levels ≥1% versus12% of patients on sunitinib compared to 26% versus 29% of patients at intermediate or poor risk in the respective treatment arms. Lees volledige artikel verder>>>>>>
24 augustus 2017: Lees ook dit artikel:
24 augustus 2017: Bron: Bristol-Myers Squibb persbericht en Journal of Clinical Oncology 33,
Ook bij gevorderde uitgezaaide nierkanker blijkt immuuntherapie met zowel alleen nivolumab (Opvio) als nivolumab in combinatie met ipilimumab (Yervoy) hoopgevende en uitstekende resultaten te geven op progressievrije ziekte en overall overleving.
Afgelopen maand gaf Bristol-Myers Squibb een persbericht uit waarin zij schrijven dat de tussenresultaten uit de Chckmate-214 fase III studie waarin patiënten opgenomen in alle stadia, sommige waren al voorbehandeld, anderen nog helemaal niet, uitstekende resultaten geven. Doel van deze studie is te kijken of deze combinatietherapie straks gegeven kan worden als eerstelijns behandeling.
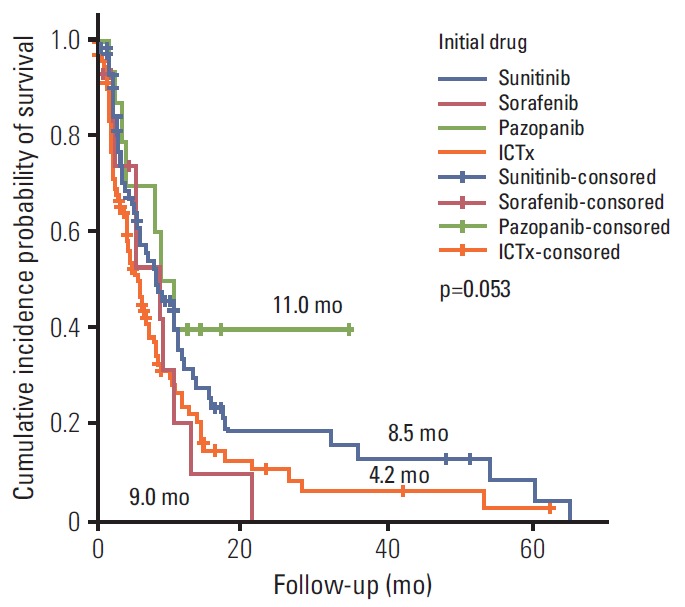
Ter vergelijking hier een grafiek van overall overleving en progressievrije ziekte met verschillende behandelingen bij niercelkanker uit deze studie: Systemic Treatments for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: 10-Year Experience of Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy waaruit zou blijken dat targeted therapie betere resultaten geeft dan immuuntherapie. Maar studies met zwaarvoorbehandelde vergevorderde kanker geven andere resultaten dan na een eerste diagnose en met weinig of geen tumorload.
(tekst loopt verder onder grafiek):
In het persbericht schrijven de mensen van BMS:
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company (NYSE: BMY) kondigt vandaag de topline resultaten aan van de CheckMate -214 trial Opdivo (nivolumab) in combinatie met Yervoy (ipilimumab) versus sunitinib bij intermediaire en laag risico patiënten met eerder onbehandelde of gevorderde of uitgezaaide niercelcarcinoom.
De combinatie voldoet aan het co-primaire einddoel van de objectieve respons (ORR) en bereikte een 41,6% ORR versus 26,5% voor sunitinib. De mediane duur van de respons is nog niet bereikt voor de combinatie van Opdivo en Yervoy en was 18,17 maanden voor sunitinib. Terwijl er een verbetering was in de voortgangsvrije overleving (PFS) (HR = 0,82, [99,1% CI 0,64-1,05], gestratificeerd 2-zijdig p = 0,03), was deze nog niet statistisch significant. De mediane PFS was 11,56 maanden (95% CI 8,71 - 15,51) voor de Opdivo en Yervoy combinatie versus 8.38 maanden (95% CI 7.03-10.81) voor sunitinib. De studie zal zoals gepland doorlopen, om het derde co-primaire einddoel van OS - overall overleving te meten. Het bijwerkrngenprofiel in de CheckMate-214 studie was consistent met dat waargenomen in eerder gemelde studies met dit doseringsschema.
Volgens het persbericht voldoet deze studie aan de verwachtingen dat nivolumab plus ipilumumab over enkele jaren eerste lijns kan wroden waar nu nivolumab al is geodgekeurd als tweedelijns voor niercelkanker.
Want in deze studie: Updated survival results from a randomized, dose-ranging phase II study of nivolumab (NIVO) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). blijkt nivolumab ook bij voorbehandelde gevorderde uitgezaaide nierkanker uitstekende resultaten te geven.
| NIVO, Q3W | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 mg/kg n = 59 | 2 mg/kg n = 54 | 10 mg/kg n = 54 | |
| Median OS, mo (80% CI) |
18.5 (16.7–NA) | 25.5 (19.8–31.2) | 24.8 (15.3–26.0) |
| OS rate, % | |||
| 12 mo | 63 | 72 | 70 |
| 24 mo | 42 | 53 | 52 |
| 36 mo | 33 | 40 | 32 |
Inmiddels is een fase III studie opgestart: Clinical trial information: NCT01354431.
Het originele persbericht kunt u lezen als u op de volgende link klikt: Bristol-Myers Squibb Announces Topline Results from CheckMate -214, a Phase 3 Study of Opdivo in Combination with Yervoy in Intermediate and Poor-Risk Patients with Previously Untreated Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Het abstract van deze studie, waarvan het volledige studierapprot gratis is in te zien: Systemic Treatments for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: 10-Year Experience of Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy staat hieronder met ook een referentielijst:
In patients with mRCC - metastatic renal cell carcinoma targeted therapy provided a better PFS and OS compared with immunotherapy
Systemic Treatments for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: 10-Year Experience of Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to compare the outcomes of first-line systemic targeted therapy (TT) and immunotherapy (IT) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC).
Materials and Methods
This study was a retrospective review of the data of 262 patients treated with systemic IT or TT with tyrosine kinase inhibitors between 2003 and 2013. The objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were assessed using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumor ver. 1.0 criteria and the Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank test.
Results
During the median 4.3-month treatment and the 24-month follow-up period, the ORR/PFS/OS of the overall first-line and second-line therapy were 41.9%/8.1 months/16.8 months and 27.5%/6.5 months/15.3 months, respectively. The first-line TT/IT/sequential IT had a PFS of 9.3/6.4/5.7 months and an OS of 15.8/16.5/40.6 months (all p < 0.05). The second-line of TT/IT had a PFS of 7.1/2.1 months (both p < 0.05) and an OS of 16.6/8.6 months (p=0.636), respectively. Pazopanib provided the best median PFS of 11.0 months (p < 0.001) and a quadruple IT regimen had a superior PFS (p=0.522). For OS, sequential treatment with IT and TT was superior compared to treatment with either IT or TT alone (40.6/16.5/15.8 months, p=0.014). The prognosis according to the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center model showed that favorable/intermediate/poor risk groups had a PFS of 8.5/10.4/2.3 months, and an OS of 43.1/20.4/5.6 months, respectively. The prognosis calculated using the Heng model showed that the favorable/intermediate/poor risk groups had a PFS of 9.2/3.9/2.7 months, and an OS of 32.4/16.5/6.1months, respectively (all p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In patients with mRCC, TT provided a better PFS and OS compared with IT.
References
References belonging to nivolumab studies
Een referentielijst van eerdere studies staat hier:
Literatur
-
1.Schmiedinger M, Bellmunt J (2010) Plethora of agents, plethora of targets, plethora of side effects in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev 36:416–424CrossRefGoogle Scholar
-
2.Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, McCann L et al (2014) Overall survival in renal-cell carcinoma with pazopanib versus sunitinib. N Engl J Med 370:1769–1780CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
-
3.Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D et al (2013) Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 369:722–731CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
-
4.Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S et al (2014) Phase II randomized trial comparing sequential first-line everolimus and second-line Sunitinib versus first-line Sunitinib and second-line Everolimus in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 32:2765–2772CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
-
5.Postow MA, Callahan MK, Wolchok JD (2014) Immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 32: 1020–1030. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.59.4358CrossRefGoogle Scholar
-
6.Michel MS, Vervenne W, de Santis M et al (2014) SWITCH study of efficacy and safety of Sorafenib/Sunitinib vs. Sunitinib/Sorafenib in the treatment of mRCC. J Clin Oncol 32(Suppl 4):393Google Scholar
-
7.Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF et al (2010) Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:711–723PubMedCentralCrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
-
8.Plimack ER, Hammers HJ, Rini BI et al (2015) Updated survival results from a randomized, dose-ranging phase II study of nivolumab (NIVO) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Clin J Oncol 33(Suppl):4553Google Scholar
Copyright information
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Poeptransplantatie vergroot effectiviteit van immuuntherapie en vermindert ernstige bijwerkingen bij uitgezaaide gevorderde niercelkanker copy 1
- Specificiteit van het menselijk leukocyten antigeen (HLA) blijkt voorspellende biomarker voor effectiviteit van immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen - checkpointremmers bij patienten met gevorderde niercelkanker
- Immuuntherapie met pembrolizumab geeft betere ziektevrije overleving (77 vs 68 procent) na operatie bij patiënten met nierkanker die een hoog risico liepen op recidief in vergelijking met een placebo
- Cabozantinib toegevoegd aan immuuntherapie met nivolumab en ipilimumab geeft betere ziekteprogressievrije tijd en ziektecontrole bij uitgezaaide onbehandelde nierkanker in vergelijking met placebo naast nivolumab en ipilimumab
- Immuuncheckpointremmers nivolumab + ipilimumab of pembrolizumab + axitinib geeft toch ziektecontrole en remissies in de klinische praktijk bij patiënten met gevorderde uitgezaaide nierkanker met een slechte prestatiestatus volgens ECOG PS ≥2
- Clostridium butyricum (CBM 588) een probioticum toegevoegd aan nivolumab plus ipilimumab verbeterd sterk de repons en progressievrije tijd voor patienten met uitgezaaide nierkanker
- Immuuntherapie met avelumab plus VEGF-remmer axitinib vermindert kans op recidief en meer ziektevrije overleving bij nierkankerpatienten (stadium III) na operatie
- Combinatiebehandelingen met vormen van immuuntherapie en anti-PD medicijnen geven veelbelovende resultaten bij (gevorderde) nierkanker. Hier de belangrijkste studies van afgelopen jaar
- Immuuntherapie met combinatiebehandeling van Nivolumab en cabozantinib als eerstelijnsbehandeling voor uitgezaaide nierkanker geeft veel betere resultaten dan stndaard behandeling sunitinib wat betreft progressievrije overleving en algehele overleving
- NLR meting - veranderende verhouding van neutrofielen tot lymfocyten - blijkt een uitstekende en eenvoudige manier om de werkzaamheid van immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen tijdens behandelingsfase te controleren. copy 1
- Immuuntherapie met Atezolizumab plus Avestin - bevacizumab geeft betere progressievrije ziekte en overall overleving dan sunitinib bij patienten met gevorderde uitgezaaide nierkanker
- Avelumab plus Axitinib geeft veel betere progressievrije overleving (plus 5 maanden) dan sunitinib als eerstelijns behandeling bij nog niet behandelde uitgezaaide nierkanker.
- Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib geeft betere overleving op 1 jaar (plus 11 procent) en betere progressievrije ziekte dan met sunitinib voor nog niet behandelde uitgezaaide nierkanker
- Nivolumab (Obvio) alleen en samen met ipilimumab (Yervoy) geeft uitstekende resultaten bij gevorderde niercelkanker ook in vergelijking met sunitinib
- Nivolumab een immuuntherapeutisch anti PD medicijn geeft uitstekende resultaten bij vergevorderde nierkanker versus everolimus en krijgt van FDA goedkeuring voor gebruik als medicijn
- immuuntherapie met axitinib (Inlyta®) en pembrolizumab (Keytruda®) bij gevorderde nog onbehandelde nierkanker verdubbelt progressievrije ziekte (10 vs 20 maanden)
- Immuuntherapie met rocapuldencel-T (AGS-003), een vorm van dendritische celtherapie met individuele T-cel stimulatie geeft uitstekende resultaten bij nieuwe patienten met uitgezaaide nierkanker
- Immuuntherapie bij nierkanker, een overzicht



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Nivolumab (Obvio) alleen en samen met ipilimumab (Yervoy) geeft uitstekende resultaten bij gevorderde niercelkanker ook in vergelijking met sunitinib"