Mocht u kanker-actueel de moeite waard vinden en ons willen ondersteunen om kanker-actueel online te houden dan kunt u ons machtigen voor een periodieke donatie via donaties: https://kanker-actueel.nl/NL/donaties.html of doneer al of niet anoniem op - rekeningnummer NL79 RABO 0372931138 t.n.v. Stichting Gezondheid Actueel in Amersfoort. Onze IBANcode is NL79 RABO 0372 9311 38
Elk bedrag is welkom. En we zijn een ANBI instelling dus uw donatie of gift is in principe aftrekbaar voor de belasting.
En als donateur kunt u ook korting krijgen bij verschillende bedrijven:
20 augustus 2017: lees ook dit artikel:
27 mei 2016: lees ook dit artikel over hetzelfde onderwerp:
27 mei 2016: Bron: CANCER: Version of Record online: 29 MAY 2015 DOI: 10.1002/cncr.29456
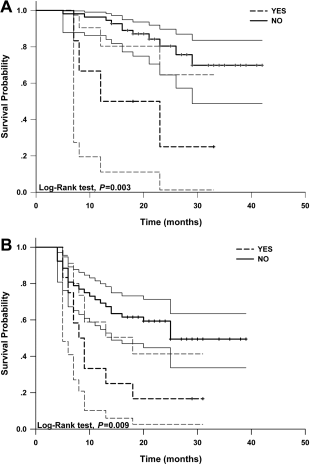
Ook deze studie (aanvullend op onderstaande studiepublicatie uit maart 2015) geeft heel goede resultaten van arsenicum trioxide gebruikt in loco regionale behandeling met leverspoelingen (o.a. TACE) van vergevorderde primaire leverkanker. Meer dan de helft van de patienten uit de groep van arsenicum triode overleefde de 25 maanden studiefollow-up: 15 patienten van de 61 overleden in de arsenicum trioxidegroep versus 34 patienten uit 64 patienten uit de controlegroep. Een onvoorstelbaar groot verschil voor een groep patienten die inoperabele leverkanker hadden en zwaar waren voorbehandeld.
Het volledige studierapport: Randomized clinical control study of locoregional therapy combined with arsenic trioxide for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. is gratis in te zien met duidlejik grafieken enz. Onder dit artikel staat het abstract ervan.
Hier een van de grafieken uit bovenstaande studie. daaronder beschrijving van andere studie
23 november 2015: lees ook dit artikel:
19 maart 2015: Bron: J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014 Dec 14. [Epub ahead of print]
Wanneer TACE - Trans Arteriële Chemo Embolisatie wordt uitgevoerd met Arseentrioxide bij primaire leverkanker met uitzaaiingen in de longen en de patiënten aanvullend daarna regelmatig intraveneuze injecties krijgen met ATO - arseentrioxide dan stijgt de mediane overleving van 2,9 maanden naar 7,3 maanden en blijkt de ziektecontrole maar liefst met 65% te verbeteren van 72,8% versus 7,2% in vergelijking met alleen TACE plus arseentrioxide. Een spectaculaire verbetering dus. Je zou je ook nog af kunnen vragen wat er gaat gebeuren als ATO intraveneus wordt vervangen / uitgebreid door ATRA - All-trans-Retionic-Acid. Of simpeler in het Nederlands een vorm van vitamine A plus kleine dosis arsenicum. Zie o.a. deze studie:
Met, ik citeer wat Francesco Lo-Coco, MD, professor in de hematologie aan de universiteit van Tor Vergata in Rome, Italië zei. Heel opmerkelijk aan deze studie is dat volgens dr. Lo-Coco het bewijs geleverd wordt dat het mogelijk is kwaadaardige kankercellen (met ATRA) te transformeren in normale cellen zonder deze te doden met chemotherapie. "Kanker is blijkbaar geen onomkeerbare toestand".
Blijkbaar werkt ATRA als een anti-PD middel. Is heel wat goedkoper dan bv. nivolumab, wat overigens ook spectaculaire resultaten laat zien bij verschillende vormen van kanker, waaronder bij melanomen:
en bij darmkanker loopt al een fase III studie in verschillende Europese landen waaronder ook Nederland: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2012-000095-42/NL.

De nieuwste studie publicatie geeft deze resultaten:
RESULTATEN:
Tussen April 2013 en June 2014, kregen 139 patienten de TACE - behandeling. 70 van hun namen deel aan de studiegroep TACE met ATO plus daarna intraveneus ATO en 69 van hun vormden de controlegroep: TACE + ATO maar zonder intraveneuze ATO. Alle patienten konden de volledige behandeling volgens het studieprotocol volgen, niemand haakte af tijdens de studieduur.
De mediane overall overleving was 7.3 maanden (95 % CI = 6.8-7.8) in de studiegroep van TACE + ATO + ATO intraveneus en 2.9 maanden (95 % CI = 2.6-3.1) in de controlegroep met alleen TACE + ATO. Dit was statistisch significant (P < 0.001). De mediane progressie vrije tijd (TTP) was 2.7 maanden (95 % CI = 1.9-3.3) voor de studiegroep van TACE + ATO + ATO intraveneus en 1.2 (95 % CI = 1.0-1.9) maanden in de controle groep (P = 0.023). Ziektecontrole DCR - Disease Control) bleek in de studiegroep van TACE + ATO + ATO intraveneus 72.85 % versus 7,24% in de controlegroep. En de onafhankelijke vastgestelde respons (ORR - objective response rate) was 7.14 %, tegenover in de controlegroep 0.00 %. DCR - ziektecontrole en ORR - onafhankelijke respons gaven dus een significant verschil te zien tussen de twee groepen (P < 0.001 en P = 0.024, respectievelijk).
Het volledige studierapport: Arsenic trioxide transarterial chemoembolization with and without additional intravenous administration of arsenic trioxide in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with lung metastasis: a single-blind, randomized trial. kunt u tegen betaling inzien.
Hier het abstract van de studie:
Arsenic trioxide transarterial chemoembolization and intravenous administration were safe and effective in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with lung metastasis.
Arsenic trioxide transarterial chemoembolization with and without additional intravenous administration of arsenic trioxide in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with lung metastasis: a single-blind, randomized trial
Locoregional therapy combined with arsenic trioxide prevents extrahepatic metastasis and prolongs the survival time for primary HCC patients
Randomized clinical control study of locoregional therapy combined with arsenic trioxide for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
The objective of this study was to determine the efficacy and safety of locoregional therapy (LRT) combined with arsenic trioxide (As2 O3 ) treatment in primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients.
METHODS:
One hundred twenty-five primary HCC patients were recruited for a randomized controlled study. Patients were randomly divided into group A (n = 61) and group B (n = 64). All patients received transarterial chemoembolization. Group A patients were given As2 O3 at 10 mg/d for 4 courses (21 days per course) with a 2-week interval between courses. Survival times, therapeutic responses, extrahepatic metastases, and adverse events were recorded.
RESULTS:
A better therapeutic response was found in group A patients, as shown by higher objective response rate (ORR) and clinical benefit rate (CBR) values in group A versus group B (ORR, 81.96% [95% confidence interval (CI), 72.32%-91.62%] vs 59.37% [95% CI, 47.34%-71.41%], χ(2) = 7.650, P < .05; CBR, 95.08% [95% CI, 89.66%-100.00%] vs 81.25% [95% CI, 71.69%-90.81%], χ(2) = 5.659, P < .05). There were fewer patients with extrahepatic metastases in group A versus group B (group A, 6 cases or 9.84% [95% CI, 2.36%-17.31%]; group B, 12 cases or 18.75% [95% CI, 9.19%-28.31%]). The survival rate for group A patients was significantly higher than that for group B patients (P < .05). No significant differences were found between the 2 groups in terms of hematology or digestive system, liver, or kidney dysfunction except for facial and limb edema.
CONCLUSIONS:
LRT combined with As2 O3 treatment prevents extrahepatic metastasis and prolongs the survival time for primary HCC patients.
© 2015 American Cancer Society.
REFERENCES
- 1
, , , et al. Global cancer facts and figure 2007. Atlanta, GA:America Cancer Society. 2007;2-3.
- 2
- 3
, , , et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1734-1739.
- 4
, , , et al. Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002;35:1164-1171.Direct Link:
- 5
, , , et al. Association of transarterial chemoembolization with survival in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Clin Oncol. 2014;2:203-206.
- 6
, , , et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in combination with radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:184-194.
- 7
, , . Transarterial chemoembolization in combination with percutaneous ablation therapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2010;30:741-749.
- 8
, , , et al. Combination therapy with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2000;89:1245-1251.
- 9
, , , . Cancer: a systems biology disease. Biosystems. 2006;83:81-90.
- 10
, , . STORM: a phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of adjuvant sorafenib after resection or ablation to prevent recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [ASCO abstract 4006]. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:5s.
- 11
, , , et al. Sorafenib down-regulates expression of HTATIP2 to promote invasiveness and metastasis of orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma tumors in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1641-1649.
- 12
, . Acute promyelocytic leukemia: what is the new standard of care? Blood Rev. 2014;28:205-212.
- 13
, , , , . Anti-hepatoma effect of arsenic trioxide on experimental liver cancer induced by 2-acetamidofluorene in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:5938-5943.
- 14
, , , , . Effect of arsenic trioxide on human hepatocarcinoma in nude mice. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:3677-3679.
- 15
. Trends in liver cancer researched by the Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. Hepatol Res. 2002;24(suppl):21-27.
- 16
, , . Report of the 15th follow-up survey of primary liver cancer. Hepatol Res. 2004;28:21-29.
- 17
, , , et al. Depletion of epithelial stem-cell compartments in the small intestine of mice lacking Tcf-4. Nat Genet. 1998;19:379-383.
- 18
, , , et al. Notch activation promotes cell proliferation and the formation of neural stem cell-like colonies in human glioma cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008;307:101-108.
- 19
, , , et al. ABCG2: determining its relevance in clinical drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:39-57.
- 20
, , , et al. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and multidrug resistance associated protein 1 (ABCC1) mediated transport by the orally administered inhibitor, CBT-1(R). Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75:1302-1312.
- 21
, , , et al. Identification of local and circulating cancer stem cells in human liver cancer. Hepatology. 2008;47:919-928.Direct Link:
- 22
, , , et al. Isolation and characterization of hepatic cancer cells with stem-like properties from hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010;19:61-67.
- 23
, . Novel therapeutic strategies for targeting liver cancer stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2011;7:517-535.
- 24
, , , et al. Arsenic trioxide sensitizes CD95/Fas-induced apoptosis through ROS-mediated upregulation of CD95/Fas by NF-kB activation. Int J Cancer. 2004;112:596-606.
- 25
, , , et al. Arsenic trioxide induces regulated, death receptor–independent cell death through a Bcl-2–controlled pathway. Oncogene. 2005;24:7031-7042.
- 26
, , , et al. Inhibition by arsenic trioxide of human hepatoma cell growth. Cancer Lett. 2002;183:147-153.
- 27
, , , et al. Arsenic trioxide–induced growth arrest of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells involving FOXO3a expression and localization. Med Oncol. 2008;26:178-185.
- 28
, , , et al. Suppression of TG-interacting factor sensitizes arsenic trioxide–induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem J. 2011;438:349-358.
- 29
, , , et al. MicroRNA expression alteration after arsenic trioxide treatment in HepG-2 cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:186-193.
- 30
, , , . Arsenic trioxide treatment of rabbit liver VX-2 carcinoma via hepatic arterial cannulation–induced apoptosis and decreased levels of survivin in the tumor tissue. Croat Med J. 2013;54:12-16.
- 31
, , , , . Combination of poly I:C and arsenic trioxide triggers apoptosis synergistically via activation of TLR3 and mitochondrial pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35:803-810.
- 32
, , . Arsenic trioxide produces polymerization of microtubules and mitotic arrest before apoptosis human tumor cell lines. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;62:529-538.
- 33
, , , et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration: a novel strategy to enhance drug-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells by a reactive oxygen species-mediated mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:37832-37839.
- 34
, , , , , . Indirect effects of Bax and Bak initiate the mitochondrial alterations that lead to cytochrome c release during arsenic trioxide–induced apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005;4:459-467.
- 35
, , , , . Arsenic trioxide–mediated oxidative stress and genotoxicity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:75-84.
- 36
, , , , , . Effects of arsenic trioxide on radiofrequency ablation of VX2 liver tumor: intraarterial versus intravenous administration. Korean J Radiol. 2012;13:195-201.
- 37
, , , , . Arsenic trioxide causes selective necrosis in solid murine tumors by vascular shutdown. Cancer Res. 1999;59:6033-6037.
- 38
- 39
, , , et al. Arsenic trioxide induces differentiation of CD133+ hepatocellular carcinoma cells and prolongs posthepatectomy survival by targeting GLI1 expression in a mouse model. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:28.
- 40
, , , et al. Multicenter phase II clinical trial of arsenic trioxide injection in the treatment of primary hepatocarcinoma [in Chinese]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011;33:697-701.
- 41
, , , , , . Arsenic trioxide in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II trial. Invest New Drugs. 2007;25:77-84.
- 42
, , , et al. The clinical therapeutic effects of arsenic trioxide combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in treating primary liver cancer with pulmonary metastases [in Chinese]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2012;51:971-974.
- 43
, , , et al. Arsenic trioxide: marked suppression of tumor metastasis potential by inhibiting the transcription factor Twist in vivo and in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140:1125-1136.
- 44
, , , et al. Global cancer facts and figure. Atlanta, GA: America Cancer Society. 2007;2–3.
Gerelateerde artikelen
- TACE met lokaal hyperthermie verdubbelde bij patienten met primaire leverkanker (HCC) (51 vs 23 procent) op 3-jaars meting in vergelijking met TACE plus lokale ethanolinjectie (PEI) copy 1
- TCM in de vorm van de Fuzheng Jiedu Xiaoji formule gegeven naast TACE - Trans Arteriele Chemo Embolisatie voor patienten met primaire leverkanker verbetert ziekteprogressievrije tijd en overleving na 1 jaar statistisch significant
- Arsenic trioxide intraveneus in combinatie met TACE geeft veel betere resultaten voor in longen uitgezaaide gevorderde primaire leverkanker dan TACE alleen copy 1
- TACE plus gemoduleerd virus - adenovirus H101 - verbetert significant ziektevrije tijd en overall overleving (plus 16 procent) in vergelijking met alleen TACE bij inoperabele primaire leverkanker stadium 4
- TACE met ATO - Arseentrioxide plus intraveneuze injecties met arseentrioxide zorgt bij primaire leverkanker met uitzaaiingen in de longen voor langere overleving - 7.3 vs 2.9 maanden - en 65 procent betere ziektecontrole
- Arsenicum trioxide (ATO) geeft significant betere resultaten naast TACE bij patiënten met primaire leverkanker met longuitzaaiingen.
- Leverkanker: Tace - Trans Arteriële Chemo Embolisatie - met zogeheten 'drug-eluting beads' levert langere ziektevrije tijd en betere kwaliteit van leven op voor patiënten met primaire leverkanker in vergelijking met directe TACE.
- Leverkanker: TACE in combinatie met RFA geeft significant betere overall overleving voor kankerpatienten met levertumoren groter dan 3 cm. (Overleving gaat mediaan van resp. 24 (alleen TACE) en 22 (alleen RFA) naar 37 maanden (TACE en RFA samen).
- Leverkanker: TACE - Trans Arteriele Chemo Embolisatie gevolgd door RFA - Radio Frequency Ablation geeft ook significant langere overleving dan alleen met TACE voor primiare levertumoren - HCC groter dan 3 cm.
- Ethanol: TACE - Transarteriële chemo-embolisatie bij inoperabele levertumoren gevolgd door injecties met ethanol geven significant langere overlevingstijd (verdubbeling van twee jaars overleving) , aldus een gerandomiseerde fase III studie.
- Ethanol: TACE - Transarteriële chemo-embolisatie bij inoperabele levertumoren gevolgd door bestraling en-of injecties met ethanol geven significant langere ziektevrije periode tussen behandelingen en gemiddeld significant langere overlevingsduur
- Ethanol en RFA - LITT - TACE: Wanneer RFA - Radio Frequency Ablation uitgevoerd wordt met aanvullend ethanol injecties (PEI) is het resultaat significant beter dan wanneer alleen RFA wordt toegepast bij verwijdering van levertumoren
- Leverkanker: Onderzoekers aan het AMC prijzen RFA, TACE , PEI en LITT en Cryosurgery aan als belangrijke behandelingsmogelijkheid voor primaire leverkanker - HCC in overzichtsstudie.
- Leverkanker: Operatie en TACE geven significant meer 5-jaars overlevingen dan palliatieve zorg voor leverkankerpatiënten. Voor patiënten van 70 jaar of ouder wordt TACE sterk afgeraden wegens slechte prognoses
- Leverkanker: TACE - Trans Arteriele Chemo Embolisatie eventueel gevolgd door RFA - Radio Frequency Ablation geeft significant betere overleving en betere kwaliteit van leven na analyse van 1126 patienten met primaire leverkanker - HCC
- Leverkanker: TACE - Trans Arteriele Chemo Embolisatie gevolgd door RFA - Radio Frequency Ablation bij primaire leverkanker - HCC geeft significant betere kwaliteit van leven dan alleen TACE
- Leverkanker: overzicht van studies met TACE - Trans Arteriele Chemo Embolisatie bij primaire leverkanker - HCC



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "TACE met ATO - Arseentrioxide plus intraveneuze injecties met arseentrioxide zorgt bij primaire leverkanker met uitzaaiingen in de longen voor langere overleving - 7.3 vs 2.9 maanden - en 65 procent betere ziektecontrole"