Helpt u ons aan 500 donateurs?
4 december 2017: In The Lancet werd in 2016 deze studie gepubliceerd: TG4010 immunotherapy and first-line chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (TIME): results from the phase 2b part of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial.
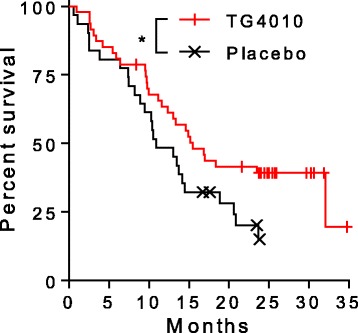
Conclusie: TG4010 plus chemotherapy seems to improve progression-free survival relative to placebo plus chemotherapy. These data support the clinical value of the TrPAL biomarker in this clinical setting; because the primary endpoint was met, the trial is to continue into the phase 3 part.
En recent werd deze studie gepubliceerd: Viral based vaccine TG4010 induces broadening of specific immune response and improves outcome in advanced NSCLC (abstract en referentielijst staat onderaan dit artikel)
Conclusie:
Our results support the causality of specific T-cell response in improved survival in NSCLC. Additionally, vaccine induced epitope spreading to other TAA participates to the enrichment of the diversity of the anti-tumor response. Hence, TG4010 appears as a useful therapeutic option to maximize response rate and clinical benefit in association with other targeted immuno-modulators.
In sommige landen worden nog patiënten aangenomen voor deze fase III studie, zie hier studieprotocol plus resultaten tot nu toe:
https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2011-001468-23/results
Zie verder hieronder d.d. 20 maart 2005
15 juni 2012: voor laatste stand van zaken betreffende immuuntherapie bij longkanker zie deze twee studies: Immuuntherapie bij gevorderde niet-klein-cellige longkanker lijkt een goede aanpak te kunnen worden in de nabije toekomst en deze: Immuuntherapie bij longkanker: overzicht van stand van zaken aan de hand van studieresultaten van laatste 10 jaar
16 december 2011: ik heb onderaan dit artikel het abstract toegevoegd van de meest recente studie - 2008 - met het longkanker vaccin MVA-Muc1-IL2 (TG4010) bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker. Met ook uit deze studie opnieuw hoopgevende resultaten aldus de onderzoekers. Het volledige studie rapport kunt u tegen betaling inzien als u hier klikt Het abstract staat onderaan dit artikel.
20 maart 2005: Bron: lungcancer update
Achtereenvolgens hier een bericht over fase II trial met een op MVA basis gebaseerd vaccin = modified vaccinia Ankara = basis van oud pokkenvaccin - bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker en daarna een abstract van studies met MVA vaccins in Frankrijk met o.a. lymfklierkanker - non-Hodgkin, melanomen en kankerpatiënten met solide tumoren, waaronder dus ook longkanker kan vallen.
Tussentijdse resultaten van een fase II klinische trial van het longkanker vaccin MVA-Muc1-IL2 - een oud pokkenvaccin - zijn bemoedigend, aldus de resultaten uit een fase II studie.. Voor de trial zijn 33 patiënten met vergevorderde of uitgezaaide niet-kleincellige longkanker geselecteerd (stadium III-B fo IV). De patiënten kregen onderhuidse injecties met MVA-Muc1-IL2 in combinatie met chemotherapie (cisplatine/vinorelbine). MVA, althans de basis daarvan is een reeds bewezen pokkenvaccin. Volgens de odnerzoerks sloeg bij 68 procent van de patiënten deze chemo-vaccin combinatie aan: bij 13 patiënten was duidelijk verminderde tumoractiviteit waarneembaar, bij 11 patiënten was de ziekte zelfs gestabiliseerd voor meer dan 12 weken. De combinatie werd goed verdragen en vertoonde nauwelijks bij effecten, althans dat beweren de onderzoekers. We kunnen ons niet vorstellen dat een chemokuur van cisplatin geen noemenswaardige bji effecten zou geven maar goed zo wordt dit beweerd. Eind 2005 staat een gerandomiseerde fase IIb trial gepland. MVA-Muc1-IL2 vaccin zal dan in een gerandomiserde studie emt meer patiënten wroden onderzocht. Naast trials bij longkankerpatiënten lopen er ook trials bij patiënten met prostaatkanker en nierkanker, ook daarvan zijn de voorlopige resultaten bemoedigend aldus een persbericht.
Transgene on Feb. 23 announced preliminary results in a multicentric phase II trial evaluating subcutaneous injections of its MVA-Muc1-IL2 vaccine. The drug was administered at a dose of 10(8) pfu with a cisplatin/vinorelbine-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic Muc1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (stage IIIB or IV). The trial sought a tumor response in at least 11 of the first 33 evaluable patients. The following responses were observed in the first 35 evaluable patients: - 13 patients responded to the treatment according to the RECIST criteria (partial responses validated in central review); and - 11 patients had their disease stabilized for more than 12 weeks. The results indicate that 24 of 35 patients (68 percent) benefited from the combination of MVA-Muc1-IL2 vaccination with chemotherapy. Good tolerance and safety of MVA-Muc1-IL2 were confirmed. Injection site reaction was the most frequent side effect. The median time to progression (TTP) exceeded six months while the median overall survival exceeded 12 months. More than half of the patients are still alive and some remain on treatment. Transgene expects to start in the last quarter of 2005 a randomized controlled Phase IIb clinical trial in combination with standard chemotherapies. In Frankrijk lopen meerdere trials met vaccin gebaserd op MVA. zie dit abstract van studeiversalg gehaald uit P{ubmed
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Oct 5;101 Suppl 2:14567-71. Epub 2004 Aug 27.
Gene-based vaccines and immunotherapeutics.
Liu M, Acres B, Balloul JM, Bizouarne N, Paul S, Slos P, Squiban P. Transgene, 11 Rue de Molsheim, 67082 Strasbourg, France. liu@transgene.fr
DNA vaccines, comprised of plasmid DNA encoding proteins from pathogens, allergens, and tumors, are being evaluated as prophylactic vaccines and therapeutic treatments for infectious diseases, allergies, and cancer; plasmids encoding normal human proteins are likewise being tested as vaccines and treatments for autoimmune diseases. Examples of in vivo prophylaxis and immunotherapy, based on different types of immune responses (humoral and cellular), in a variety of disease models and under evaluation in early phase human clinical trials are presented. Viral vectors continue to show better levels of expression than those achieved by DNA plasmid vectors. We have focused our clinical efforts, at this time, on the use of recombinant viral vectors for both vaccine as well as cytokine gene transfer studies.
We currently have four clinical programs in cancer immunotherapy. Two nonspecific immunotherapy programs are underway that apply adenoviral vectors for the transfer of cytokine genes into tumors in situ. An adenovirus-IFN gamma construct (TG1042) is currently being tested in phase II clinical trials in cutaneous lymphoma. A similar construct, adenovirus-IL2 (TG1024), also injected directly into solid tumors, is currently being tested in patients with solid tumors (about one-half of which are melanoma). Encouraging results are seen in both programs. Two cancer vaccine immunotherapy programs focus on two cancer-associated antigens: human papilloma virus E6 and E7 proteins and the epithelial cancer-associated antigen MUC1. Both are encoded by a highly attenuated vaccinia virus vector [modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA)] and both are coexpressed with IL-2. Encouraging results seen in both of these programs are described.
PMID: 15333750 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
The combination of TG4010 vaccin with standard chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer is feasible and shows encouraging results
A phase II study of Tg4010 (Mva-Muc1-Il2) in association with chemotherapy in patients with stage III/IV Non-small cell lung cancer.
Source
Regional Center for Lung Disease, Wielkopolskie Centrum, Poznan, Poland. rramlau@onet.eu
Erratum in
- J Thorac Oncol. 2008 Aug;3(8):941.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
TG4010 is a recombinant viral vector expressing both the tumor-associated antigen MUC1 and Interleukine-2. This vector is based on the modified virus of Ankara, a significantly attenuated strain of vaccinia virus. TG4010 has been designed to induce or amplify a cellular immune response directed against tumor cells expressing MUC1.
METHODS:
A multicenter, randomized phase II study has explored two schedules of the combination of TG4010 with first line chemotherapy in patients with stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer. In Arm 1, TG4010 was combined upfront with cisplatin (100 mg/m day 1) and vinorelbine (25 mg/m day 1 and day 8). In Arm 2, patients were treated with TG4010 monotherapy until disease progression, followed by TG4010 plus the same chemotherapy as in Arm1. Response rate was evaluated according to RECIST. Median time to progression and median overall survival were calculated according to the Kaplan-Meier method.
RESULTS:
Sixty-five patients were enrolled, 44 in Arm 1 and 21 in Arm 2, in accordance with the two stage Simon design of the statistical plan. In Arm 1, partial response was observed in 13 patients out of 37 evaluable patients (29.5% of the intent to treat population, 35.1% of the evaluable patients). In Arm 2, two patients experienced stable disease for more than 6 months with TG4010 alone (up to 211 days), in the subsequent combination with chemotherapy, one complete and one partial response were observed out of 14 evaluable patients. Arm 2 did not meet the criteria for moving forward to second stage. The median time to progression was 4.8 months for Arm 1. The median overall survival was 12.7 months for Arm 1 and 14.9 for Arm 2. One year survival rate was 53% for Arm 1 and 60% for Arm 2. TG4010 was well tolerated, mild to moderate injection site reactions, flu-like symptoms, and fatigue being the most frequent adverse reactions. A MUC1-specific cellular immune response was observed in lymphocyte samples from all responding patients evaluable for immunology.
CONCLUSIONS:
The combination of TG4010 with standard chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer is feasible and shows encouraging results. A randomized study evaluating the addition of TG4010 to first line chemotherapy in this population is in progress.
- PMID:
- 18594319
- [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Our results support the causality of specific T-cell response in improved survival in NSCLC. Additionally, vaccine induced epitope spreading to other TAA participates to the enrichment of the diversity of the anti-tumor response. Hence, TG4010 appears as a useful therapeutic option to maximize response rate and clinical benefit in association with other targeted immuno-modulators.
Viral based vaccine TG4010 induces broadening of specific immune response and improves outcome in advanced NSCLC
Abstract
Background
Advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving TG4010, a therapeutic viral vaccine encoding human Mucin 1 and interleukin-2 in addition to standard chemotherapy, displayed longer overall survival in comparison to that of patients treated with standard chemotherapy alone. Our study intended to establish the association between overall survival and vaccine-induced T cell responses against tumor associated antigens (TAA) targeted by the vaccine.
Method
The TIME trial was a placebo-controlled, randomized phase II study aimed at assessing efficacy of TG4010 with chemotherapy in NSCLC. 78 patients from the TIME study carrying the HLA-A02*01 haplotype were analyzed using combinatorial encoding of MHC multimers to detect low frequencies of cellular immune responses to TG4010 and other unrelated TAA.
Results
We report that improvement of survival under TG4010 treatment correlated with development of T cell responses against MUC1. Interestingly, responses against MUC1 were associated with broadening of CD8 responses against non-targeted TAA, thus demonstrating induction of epitope spreading.
Conclusion
Our results support the causality of specific T-cell response in improved survival in NSCLC. Additionally, vaccine induced epitope spreading to other TAA participates to the enrichment of the diversity of the anti-tumor response. Hence, TG4010 appears as a useful therapeutic option to maximize response rate and clinical benefit in association with other targeted immuno-modulators.
Trial registration
Registered on ClinicalTrials.gov under identifier NCT01383148 on June 23rd, 2011.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0274-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
References
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Poeptransplantatie - Fecale Microbiota Transplantatie (FMT) vergroot effectiviteit van immuuntherapie bij niet-kleincellige longkanker en melanomen
- Immuuntherapie plus chemotherapie in de ochtend geeft veel betere overleving (plus 13 maanden) in vergelijking met toediening in de middag bij patiënten met niet-kleincellige longkanker
- CAN-2409, een virale vorm van immuuntherapie verlengt mediane overleving van patiënten met niet-operable stadium III/IV niet-kleincellig longkanker na falen immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen
- Pumitamig, een bispecifieke antilichaam, naast chemotherapie geeft uitstekende resultaten bij patienten met gevorderde kleincellige longkanker
- Atezolizumab geeft bij patienten met longkanker bij wie dubbele platina chemotherapie niet mogelijk was verdubbeling van overall overleving (24 vs 12 procent) in vergelijking met enkelvoudige chemokuur
- Immuuntherapie met pembrolizumab vooraf aan operatie bij niet kleincellige longkanker stadium II en III gevolgd door onderhoudsdosis pembrolizumab verbetert ziektevrije tijd in vergelijking met placebo op 2 jaars meting
- Immuuntherapie met 2 kuren nivolumab - OPDIVO vooraf aan operatie bij operabele longkanker bereikt op 5-jaars meting 80 procent overall overleving en 60 procent recidiefvrije overleving.
- Immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen als eerstelijns geeft zelfde of nog betere resultaten dan gecombineerd met chemotherapie op platinabasis bij niet-kleincellige longkanker
- Imfinzi (durvalumab) een immuuntherapeutisch medicijn is in lagere dosis en minder frequent gegeven net zo effectief bij longkanker stadium III en gevorderde blaaskanker. FDA geeft hieraan goedkeuring.
- Nivolumab naast carboplatine en etoposide (CE) geeft als eerstelijnsbehandeling voor gevorderde kleincellige longkanker betere resultaten in overall overleving vergelijking met alleen chemo
- Pembrolizumab geeft betere resultaten dan docetaxel bij patiënten met al eerder behandelde niet-kleincellige longkanker op 3-jaars meting na 2 jaar pembrolizumab. 35 vs 13 procent overall overleving.
- Combinatiebehandeling van Bemcentinib en Pembrolizumab geeft alsnog uitstekende resultaten (40 procent PR of CR) patienten met niet-kleincellige longkanker waar chemo faalde. copy 1
- immuuntherapie met pembrolizumab na lokale operatie of stereotactische bestraling van uitgezaaide niet-kleincellige longkanker geeft veel betere overall overleving dan statistisch cijfers
- immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijn nivolumab bij uitgezaaide longkanker stadium IV geeft nagenoeg gelijke overall overleving maar met veel minder bijwerkingen dan chemotherapie
- Immuuntherapie met alleen Pembrolizumab geeft betere overall overleving in vergelijking met chemo voor onbehandelde patienten met uitgezaaide niet-kleincellige longkanker. Ook bij patienten met weinig PD-L1–Expressie
- Immuuntherapie met de combinatie van pembrolizumab plus Entinostat, een HDAC-remmer, geeft alsnog bij patienten met klein-cellige longkanker een respons die eerder met anti-PD toch ziekteprogressie lieten zien
- Immuuntherapie met Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) geeft betere resultaten dan chemotherapie als eerstelijns behandeling bij uitgezaaide gevorderde niet-kleincellige longkanker met PD-1 mutatie
- Immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen: Unraveling PD-L1 Assays in NSCLC: Are They Interchangeable?
- Pembrolizumab een anti-PD medicijn geeft betere 1 jaars overleving 70% vs 54%.dan chemo en de heflt minder ernstige bijwerkingen bij onbehandelde gevorderde niet-kleincellige longkanker.
- PD-L1 Inhibition With Atezolizumab (MPDL3280A) for Solid Tumors
- Durvalumab (IMFINZI) geeft bij uitgezaaide niet-klein-cellige longkanker 11 maanden meer progressievrije tijd (44 procent) en FDA geeft durvalumab goedkeuring
- Dendritische celtherapie plus gemoduleerde T-cellen naast chemo geeft 25 procent betere mediane overall overleving op 5 jaar bij operabele niet-kleincellige longkanker copy 1
- CIMAvax-EGF vaccin geeft uitstekende resultaten op overall overleving en ziektevrije tijd bij longkanker en andere vormen van kanker met EGFR mutatie copy 1
- Immuuntherapie met T-car cells - Tumor Lymphocytic Infiltration is interessante ontwikkeling bij verschillende vormen van kanker. Hoe meer TLI hoe beter copy 1
- Immuuntherapie met Nivolumab (Opdivo) geeft geen statistisch verschil in overleving met chemo bij onbehandelde longkanker
- Immuuntherapie met bacterie naast chemo zorgt voor zeer goede resultaten bij inoperabele mesothelioma met ziektecontrole van 90 procent
- Immuuntherapie en gerichte therapie bij longkanker zijn de beste opties, maar wat zijn de verschillen en wanneer deze in te zetten?
- Nivolumab - Opdivo geeft hoopvolle resultaten bj zwaar voorbehandelde, uitgezaaide niet-klein-cellige longkanker met alsnog enkele duurzame totale remissies
- MAGE-A3 vaccin leek hoopvol voor niet-klein-cellige longkanker, maar faalt in fase III studie en studie wordt stopgezet door GSK
- Immuuntherapie met monoklonaal middel - codenaam MPDL3280A geeft bijzonder goede resultaten in fase I studie met 53 patienten met niet-klein-cellige longkanker
- Immuuntherapie bij gevorderde niet-klein-cellige longkanker lijkt een goede aanpak te kunnen worden in de nabije toekomst.
- Immuuntherapie bij longkanker: overzicht van stand van zaken aan de hand van studieresultaten van laatste 10 jaar
- Immuuntherapie bij longkanker: 131I-chTNT een antibody medicijn rechtstreeks ingespoten in de tumoren bij inoperable longkankerpatiënten zorgt voor opmerkelijke resultaten in fase I en II studies
- Immuuntherapie: 131I-chTNT een antibody medicijn rechtstreeks ingespoten in de tumoren bij inoperable longkankerpatiënten zorgt opnieuw voor opmerkelijke resultaten in Fase I-II studies.N.
- Telcyta, een immuuntherapeutisch middel zorgt voor goede resultaten in fase II trials bij patienten met niet-klein-cellige longkanker
- GVAX - een vaccin - lijkt effectief bij vergevorderde longkanker, aldus studie onder 43 patiënten gedurende drie jaar.
- Vaccin MVA-Muc1-IL2 - TG4010 - bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker geeft bemoedigende resultaten. Recente fase II studie bevestigt goede resultaten
- Vaccin gemaakt op basis van epidermal growth factor (EGF) geeft significant meer overlevingen en significant betere kwaliteit van leven bij patienten met vergevorderde niet-klein-cellige longkanker, (stadium IIIB en IV)
- Vaccinatie met Bec2/bacille Calmette-Guerin bij longkanker stadium I en II geeft geen enkel effect op langere ziektevrije tijd of overall overleving aldus gerandomiseerde fase III studie uitgevoerd mede door Nederlandse ziekenhuizen
- Immuuntherapie en vaccinaties bij longkanker: een overzicht van belangrijke studies en artikelen en recente ontwikkelingen.



 #1 and
#1 and
Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Vaccin MVA-Muc1-IL2 - TG4010 - bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker geeft bemoedigende resultaten. Recente fase II studie bevestigt goede resultaten"