Aan dit artikel is vele uren gewerkt. Opzoeken, vertalen, op de website plaatsen enz. Als u ons wilt ondersteunen dan kan dat via een al of niet anonieme donatie. Elk bedrag is welkom hoe klein ook. Klik hier als u ons wilt helpen kanker-actueel online te houden. Wij zijn een ANBI organisatie en dus is uw donatie in principe aftrekbaar voor de belasting.
4 februari 2016: Lees: Minister Schippers heeft nivolumab voor gevorderde longkanker in het basispakket opgenomen per 1 maart 2016.
10 mei 2015: Bron: Journal of Clinical Oncology
Nivolumab, een anti PD-medicijn (PD = programmed Death) zorgt voor spectaculaire resultaten bij zwaar voorbehandelde niet-kleincellige longkanker. Aldus een fase I/II studie met totaal 126 patiënten met uitgezaaide vergevorderde niet-klein-cellige longkanker.
Overall overleving:
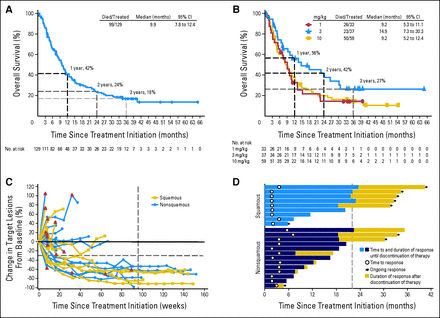
Mediane overall overleving voor alle gebruikte doses was 9.9 maanden, met 1-jaars, 2-jaars, en 3-jaars overleving van respectievelijk 42%, 24% en 18%. Let wel dit is een grope patiënten die in het eindstadium van hun ziekte verkeerden. Dat dan nog 18% de 3 jaar overleeft is wel heel bijzonder voor niet-klein-cellige longkanker. Onder de patiënten met plaveiselcarcinoom en niet-plaveisel carcinoom karakter was de mediane overall overleving respectievelijk 9.2 maanden en 10.1 maanden, met 1-jaars, 2-jaars, en 3-jaars overleving van 41%, 24%, en 19% en 42%, 27%, en 16% respectievelijk. Onder de 37 patiënten die de hoogste dosering van 3 mg/kg, hadden ontvangen bleek de 1-jaars, 2-jaars, en 3-jaars overeleving resepctievelijk 56%, 42%, en 27%. Dus bijna 1 op de 3 patiënten die de hoogste dosis nivolumab hadden ontvangen leefden nog na drie jaar. Dit is ongehoord voor deze groep van patiënten.
Ik zal komende dagen de studieresultaten nog verder vertalen maar heb nu te weinig tijd daarvoor. Maar zie dit volledige studie rapport: Overall Survival and Long-Term Safety of Nivolumab (Anti–Programmed Death 1 Antibody, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer kunt u gratis inzien.
Het abstract staat onderaan dit artikel maar hier de studieresultaten uit het originele studierapport..
Study Details
In the study, 129 patients with advanced NSCLC enrolled from 12 U.S. sites between November 2008 and January 2012 received nivolumab 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg intravenously once every 2 weeks in 8-week cycles for up to 96 weeks. Tumor burden was assessed (RECIST version 1.0) after each cycle. Patients had to have one to five prior systemic treatments for advanced NSCLC, progression on at least one platinum- or taxane-based regimen, and at least one measurable lesion.
Patients had a median age of 65 years (range = 38–85 years), 61% were male, 98% had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1, and histology was nonsquamous in 58% and squamous in 42%. The number of prior systemic treatments was one or two in 46% and three or more in 54%; prior treatment included platinum-based therapy in 99%, tyrosine kinase inhibitors in 28%, surgery in 66%, radiotherapy in 58%, and hormonal, immunologic, or biologic therapy in 12%. EGFR mutation status was mutant in 9%, wild-type in 43%, and unknown in 47%; and KRAS mutation status was mutant in 16%, wild-type in 28%, and unknown in 56%.
Response Rates
Median follow-up was 39 months. Across all nivolumab dose levels, the objective response rate was 17.1% among all patients, including response rates of 16.7% in patients with squamous histology and 17.6% in those with nonsquamous histology. Response rates in patients receiving the 3-mg/kg dose selected for further development were 24.3% among all patients, including 22.2% in those with squamous histology and 26.3% in those with nonsquamous histology. Median duration of response among all responders was 17.0 months (range = 1.4+ to 36.8+ months), including median duration not reached in patients with squamous NSCLC, 14.2 months in those with nonsquamous histology, and 17.0 months in those receiving 3 mg/kg.
Eleven (50%) of the 22 responses were documented at the first 8-week tumor assessment. Median progression-free survival in responders was 20.6 months (range = 4.7+ to 40.3+ months). Response was ongoing in 41% of responders at the time of analysis. Among 18 responders who discontinued nivolumab for reasons other than disease progression, 9 (50%) had responses of over 9 months after the end of treatment. Stable disease of 24 weeks or more was observed in an additional 10% of patients.
Overall Survival
Median overall survival across all doses was 9.9 months, with 1-, 2-, and 3-year rates of 42%, 24%, and 18%. Among patients with squamous and nonsquamous histology, median overall survival was 9.2 months and 10.1 months, with 1-, 2-, and 3-year rates of 41%, 24%, and 19% and 42%, 27%, and 16%. Among 37 patients receiving 3 mg/kg, 1-, 2-, and 3-year survival rates were 56%, 42%, and 27%.
Immune-Pattern Responses
Unconventional immune-pattern responses—ie, persistent reduction in target lesions in the presence of new lesions or regression of target lesions after initial growth—were observed in an additional six patients (5%). Overall survival in these patients was 7.3, 11.2, 16.7, 26.7, 34.5+ (ongoing), and 54.3+ months at the time of analysis.
Toxicity
The most common treatment-related adverse events of any grade were fatigue (24%), decreased appetite (12%), and diarrhea (10%). Treatment-related grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 14%, with fatigue (3%) being most common. Any-grade treatment-related adverse events of special interest included skin events in 15% of patients, gastrointestinal events in 12%, and pulmonary events in 7%. Grade ≥ 3 pneumonitis occurred in four patients (3%). Death considered related to treatment occurred in three patients (2%), in association with pneumonitis in each.
The investigators concluded: “Nivolumab monotherapy produced durable responses and encouraging survival rates in patients with heavily pretreated NSCLC. Randomized clinical trials with nivolumab in advanced NSCLC are ongoing.” Ongoing phase III trials include comparisons of nivolumab vs docetaxel in previously treated advanced squamous and advanced nonsquamous NSCLC and a comparison vs platinum-based therapy in previously untreated advanced PD-L1–positive disease.
Scott N. Gettinger, MD, of Yale Cancer Center, is the corresponding author for the Journal of Clinical Oncology article.
The study was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono Pharmaceutical. For full disclosures of the study authors, visit jco.ascopubs.org.
Nivolumab monotherapy produced durable responses and encouraging survival rates in patients with heavily pretreated NSCLC. Randomized clinical trials with nivolumab in advanced NSCLC are ongoing.
- © 2015 by American Society of Clinical Oncology
Overall Survival and Long-Term Safety of Nivolumab (Anti–Programmed Death 1 Antibody, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- Scott N. Gettinger⇑,
- Leora Horn,
- Leena Gandhi,
- David R. Spigel,
- Scott J. Antonia,
- Naiyer A. Rizvi,
- John D. Powderly,
- Rebecca S. Heist,
- Richard D. Carvajal,
- David M. Jackman,
- Lecia V. Sequist,
- David C. Smith,
- Philip Leming,
- David P. Carbone,
- Mary C. Pinder-Schenck,
- Suzanne L. Topalian,
- F. Stephen Hodi,
- Jeffrey A. Sosman,
- Mario Sznol,
- David F. McDermott,
- Drew M. Pardoll,
- Vindira Sankar,
- Christoph M. Ahlers,
- Mark Salvati,
- Jon M. Wigginton,
- Matthew D. Hellmann,
- Georgia D. Kollia,
- Ashok K. Gupta and
- Julie R. Brahmer
+ Author Affiliations
- Corresponding author: Scott N. Gettinger, MD, Yale Cancer Center, 333 Cedar St, FMP127, New Haven, CT 06520; e-mail: scott.gettinger@yale.edu.
-
Presented in part at the 49th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), Chicago, IL, May 31-June 4, 2013; the 15th World Conference on Lung Cancer, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, October 27-30, 2013; the 50th ASCO Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, May 30-June 3, 2014; and the Chicago Multidisciplinary Symposium in Thoracic Oncology, Chicago, IL, October 30-November 1, 2014.
Abstract
Purpose Programmed death 1 is an immune checkpoint that suppresses antitumor immunity. Nivolumab, a fully human immunoglobulin G4 programmed death 1 immune checkpoint inhibitor antibody, was active and generally well tolerated in patients with advanced solid tumors treated in a phase I trial with expansion cohorts. We report overall survival (OS), response durability, and long-term safety in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receiving nivolumab in this trial.
Patients and Methods Patients (N = 129) with heavily pretreated advanced NSCLC received nivolumab 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg intravenously once every 2 weeks in 8-week cycles for up to 96 weeks. Tumor burden was assessed by RECIST (version 1.0) after each cycle.
Results Median OS across doses was 9.9 months; 1-, 2-, and 3-year OS rates were 42%, 24%, and 18%, respectively, across doses and 56%, 42%, and 27%, respectively, at the 3-mg/kg dose (n = 37) chosen for further clinical development. Among 22 patients (17%) with objective responses, estimated median response duration was 17.0 months. An additional six patients (5%) had unconventional immune-pattern responses. Response rates were similar in squamous and nonsquamous NSCLC. Eighteen responding patients discontinued nivolumab for reasons other than progressive disease; nine (50%) of those had responses lasting > 9 months after their last dose. Grade 3 to 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 14% of patients. Three treatment-related deaths (2% of patients) occurred, each associated with pneumonitis.
Conclusion Nivolumab monotherapy produced durable responses and encouraging survival rates in patients with heavily pretreated NSCLC. Randomized clinical trials with nivolumab in advanced NSCLC are ongoing.
Gerelateerde artikelen
- Poeptransplantatie - Fecale Microbiota Transplantatie (FMT) vergroot effectiviteit van immuuntherapie bij niet-kleincellige longkanker en melanomen
- Immuuntherapie plus chemotherapie in de ochtend geeft veel betere overleving (plus 13 maanden) in vergelijking met toediening in de middag bij patiënten met niet-kleincellige longkanker
- CAN-2409, een virale vorm van immuuntherapie verlengt mediane overleving van patiënten met niet-operable stadium III/IV niet-kleincellig longkanker na falen immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen
- Pumitamig, een bispecifieke antilichaam, naast chemotherapie geeft uitstekende resultaten bij patienten met gevorderde kleincellige longkanker
- Atezolizumab geeft bij patienten met longkanker bij wie dubbele platina chemotherapie niet mogelijk was verdubbeling van overall overleving (24 vs 12 procent) in vergelijking met enkelvoudige chemokuur
- Immuuntherapie met pembrolizumab vooraf aan operatie bij niet kleincellige longkanker stadium II en III gevolgd door onderhoudsdosis pembrolizumab verbetert ziektevrije tijd in vergelijking met placebo op 2 jaars meting
- Immuuntherapie met 2 kuren nivolumab - OPDIVO vooraf aan operatie bij operabele longkanker bereikt op 5-jaars meting 80 procent overall overleving en 60 procent recidiefvrije overleving.
- Immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen als eerstelijns geeft zelfde of nog betere resultaten dan gecombineerd met chemotherapie op platinabasis bij niet-kleincellige longkanker
- Imfinzi (durvalumab) een immuuntherapeutisch medicijn is in lagere dosis en minder frequent gegeven net zo effectief bij longkanker stadium III en gevorderde blaaskanker. FDA geeft hieraan goedkeuring.
- Nivolumab naast carboplatine en etoposide (CE) geeft als eerstelijnsbehandeling voor gevorderde kleincellige longkanker betere resultaten in overall overleving vergelijking met alleen chemo
- Pembrolizumab geeft betere resultaten dan docetaxel bij patiënten met al eerder behandelde niet-kleincellige longkanker op 3-jaars meting na 2 jaar pembrolizumab. 35 vs 13 procent overall overleving.
- Combinatiebehandeling van Bemcentinib en Pembrolizumab geeft alsnog uitstekende resultaten (40 procent PR of CR) patienten met niet-kleincellige longkanker waar chemo faalde. copy 1
- immuuntherapie met pembrolizumab na lokale operatie of stereotactische bestraling van uitgezaaide niet-kleincellige longkanker geeft veel betere overall overleving dan statistisch cijfers
- immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijn nivolumab bij uitgezaaide longkanker stadium IV geeft nagenoeg gelijke overall overleving maar met veel minder bijwerkingen dan chemotherapie
- Immuuntherapie met alleen Pembrolizumab geeft betere overall overleving in vergelijking met chemo voor onbehandelde patienten met uitgezaaide niet-kleincellige longkanker. Ook bij patienten met weinig PD-L1–Expressie
- Immuuntherapie met de combinatie van pembrolizumab plus Entinostat, een HDAC-remmer, geeft alsnog bij patienten met klein-cellige longkanker een respons die eerder met anti-PD toch ziekteprogressie lieten zien
- Immuuntherapie met Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) geeft betere resultaten dan chemotherapie als eerstelijns behandeling bij uitgezaaide gevorderde niet-kleincellige longkanker met PD-1 mutatie
- Immuuntherapie met anti-PD medicijnen: Unraveling PD-L1 Assays in NSCLC: Are They Interchangeable?
- Pembrolizumab een anti-PD medicijn geeft betere 1 jaars overleving 70% vs 54%.dan chemo en de heflt minder ernstige bijwerkingen bij onbehandelde gevorderde niet-kleincellige longkanker.
- PD-L1 Inhibition With Atezolizumab (MPDL3280A) for Solid Tumors
- Durvalumab (IMFINZI) geeft bij uitgezaaide niet-klein-cellige longkanker 11 maanden meer progressievrije tijd (44 procent) en FDA geeft durvalumab goedkeuring
- Dendritische celtherapie plus gemoduleerde T-cellen naast chemo geeft 25 procent betere mediane overall overleving op 5 jaar bij operabele niet-kleincellige longkanker copy 1
- CIMAvax-EGF vaccin geeft uitstekende resultaten op overall overleving en ziektevrije tijd bij longkanker en andere vormen van kanker met EGFR mutatie copy 1
- Immuuntherapie met T-car cells - Tumor Lymphocytic Infiltration is interessante ontwikkeling bij verschillende vormen van kanker. Hoe meer TLI hoe beter copy 1
- Immuuntherapie met Nivolumab (Opdivo) geeft geen statistisch verschil in overleving met chemo bij onbehandelde longkanker
- Immuuntherapie met bacterie naast chemo zorgt voor zeer goede resultaten bij inoperabele mesothelioma met ziektecontrole van 90 procent
- Immuuntherapie en gerichte therapie bij longkanker zijn de beste opties, maar wat zijn de verschillen en wanneer deze in te zetten?
- Nivolumab - Opdivo geeft hoopvolle resultaten bj zwaar voorbehandelde, uitgezaaide niet-klein-cellige longkanker met alsnog enkele duurzame totale remissies
- MAGE-A3 vaccin leek hoopvol voor niet-klein-cellige longkanker, maar faalt in fase III studie en studie wordt stopgezet door GSK
- Immuuntherapie met monoklonaal middel - codenaam MPDL3280A geeft bijzonder goede resultaten in fase I studie met 53 patienten met niet-klein-cellige longkanker
- Immuuntherapie bij gevorderde niet-klein-cellige longkanker lijkt een goede aanpak te kunnen worden in de nabije toekomst.
- Immuuntherapie bij longkanker: overzicht van stand van zaken aan de hand van studieresultaten van laatste 10 jaar
- Immuuntherapie bij longkanker: 131I-chTNT een antibody medicijn rechtstreeks ingespoten in de tumoren bij inoperable longkankerpatiënten zorgt voor opmerkelijke resultaten in fase I en II studies
- Immuuntherapie: 131I-chTNT een antibody medicijn rechtstreeks ingespoten in de tumoren bij inoperable longkankerpatiënten zorgt opnieuw voor opmerkelijke resultaten in Fase I-II studies.N.
- Telcyta, een immuuntherapeutisch middel zorgt voor goede resultaten in fase II trials bij patienten met niet-klein-cellige longkanker
- GVAX - een vaccin - lijkt effectief bij vergevorderde longkanker, aldus studie onder 43 patiënten gedurende drie jaar.
- Vaccin MVA-Muc1-IL2 - TG4010 - bij niet-klein-cellige longkanker geeft bemoedigende resultaten. Recente fase II studie bevestigt goede resultaten
- Vaccin gemaakt op basis van epidermal growth factor (EGF) geeft significant meer overlevingen en significant betere kwaliteit van leven bij patienten met vergevorderde niet-klein-cellige longkanker, (stadium IIIB en IV)
- Vaccinatie met Bec2/bacille Calmette-Guerin bij longkanker stadium I en II geeft geen enkel effect op langere ziektevrije tijd of overall overleving aldus gerandomiseerde fase III studie uitgevoerd mede door Nederlandse ziekenhuizen
- Immuuntherapie en vaccinaties bij longkanker: een overzicht van belangrijke studies en artikelen en recente ontwikkelingen.



Plaats een reactie ...
Reageer op "Nivolumab - Opdivo geeft hoopvolle resultaten bj zwaar voorbehandelde, uitgezaaide niet-klein-cellige longkanker met alsnog enkele duurzame totale remissies"